SQL
Structured Query Language, or SQL, is the primary programming language used to manage and interact with relational databases. SQL can perform various operations such as creating, updating, reading, and deleting records within a database.
SQL is just a query language. You typically use it to interact with a specific database technology. For example:
Although many different databases use the SQL language, most of them will have their own dialect. It's critical to understand that not all databases are created equal. Just because one SQL-compatible database does things a certain way, doesn't mean every SQL-compatible database will follow those exact same patterns.
There are more differences, for instance SQLite is a serverless database management system (DBMS) that has the ability to run within applications, whereas PostgreSQL uses a Client-Server model and requires a server to be installed and listening on a network, similar to an HTTP server.
Some databases like SQLite have a loose type system where you can store any type of data in any column, whereas other databases like PostgreSQL have a strict type system where you must specify the type of data you want to store in a column.
Relational databases
A relational database is a type of database that stores data so that it can be easily related to other data. Let's take Twitter as an example: a user can have many tweets. There's a relationship between a user and their tweet.
In a relational database:
- Data is typically represented in "tables"
- Each table has "columns" or "fields that hold attributes related to the record
- Each row or entry in the table is called a record
- Typically, each record has a unique
Idcalled the primary key
Example of a relational database
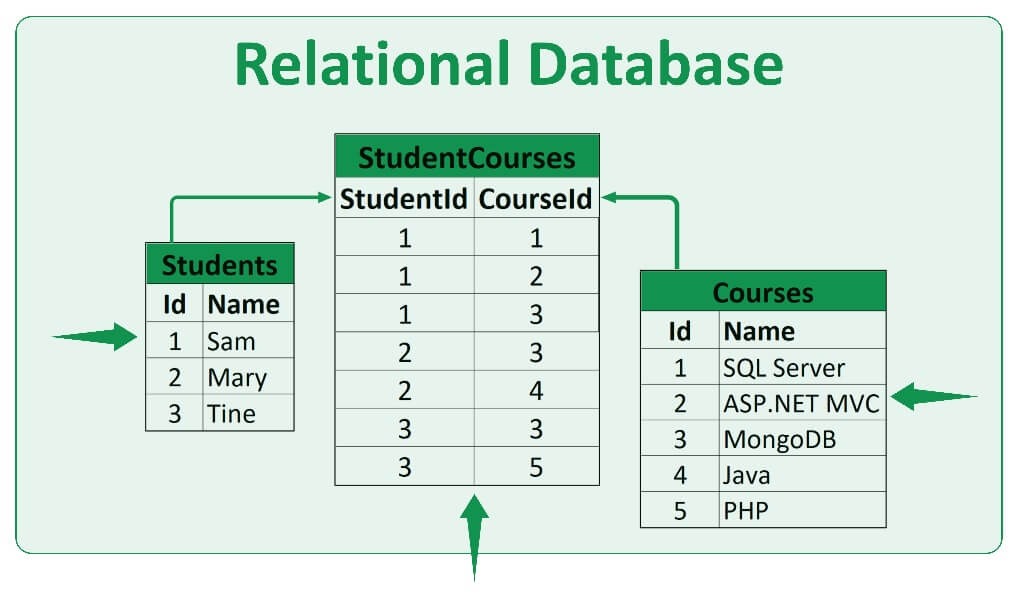
Here is an example of a small relational database. This database has 3 tables, Students, Courses, and StudentCourses. The StudentCourses table manages the relationship between the Students and the Courses tables.
If we want to find the courses for the student 'Sam', we can do it by looking in the StudentCourses for the records that match his StudentId.