CKA Exam Questions
Scale a deployment
kubectl scale deployment <deployment-name> --replicas=<number>
Create a NodePort service for a deployment
kubectl expose deployment <deployment-name> --type=NodePort <service-name>
Create a PersistentVolume
Create a PersistentVolume named my-pv with access mode ReadWriteOnce and size 10Gi using hostPath
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: my-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 10Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
hostPath:
path: /data/my-pv
Creating an Ingress resource
Create an Ingress resource named luau that routes traffic on the path /aloha to the aloha service on port 54321
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: luau
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /aloha
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: aloha
port:
number: 54321
Monitor cluster and application resources
- Identify all Pods in the integration namespace with the label
app=intensive - Determine which of these Pods is using the most CPU resources
- Write the name of the Pod consuming the most CPU resources to /opt/cka/answers/cpu_pod_01.txt
kubectl top pods -n integration # List all pods in the integration namespace and their CPU usage
kubectl get pods -n integration -L app=intensive # List pods with label app=intensive
Configure Pod admission and scheduling
- Create a Pod named noded that uses the nginx image
- Ensure the Pod is scheduled to a node labeled disk=nvme
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: noded
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
nodeSelector:
disk: nvme
Multicontainer Pod
- Create a pod named multicontainer that has two containers:
- A container running the redis:6.2.6 image
- A container running the nginx:1.21.6 image
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: multicontainer
spec:
containers:
- name: redis
image: redis:6.2.6
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.21.6
Monitor logs of a container
kubectl logs <pod-name> -c <container-name>
Add a sidecar container which runs a specific bash command
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: logger
spec:
containers:
- name: loggingpod
image: busybox
args: [/bin/sh, -c, "i=0; while true; do echo '$i: $(date)' >> /var/log/log01.log; i=$((i+1)); sleep 10; done"]
volumeMounts:
- name: logz
mountPath: /var/log
- name: sidecar
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c", "tail -f /var/log/log01.log"]
volumeMounts:
- name: logz
mountPath: /var/log
volumes:
- name: logz
emptyDir: {}
nodeName: node-1
Manage role based access control
- Create a ClusterRole named app-creator that allows create permissions for Deployments, StatefulSets, and DaemonSets
- Create a ServiceAccount named app-dev
- Bind the ServiceAccount app-dev to the ClusterRole app-creator using a ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: app-creator
rules:
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["deployments", "statefulsets", "daemonsets"]
verbs: ["create"]
To find out which apiGroups are available, you can use the command:
kubectl api-resources | grep Stateful # Will show that StatefulSets belong to apps/v1
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: app-dev
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: app-dev-binding
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: app-dev
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: app-creator
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Troubleshoot cluster with taints
- Inspect the nodes controller and node-1 for any taints they have. Write the results to heir respective files
kubectl describe node controller | grep -i Taints
kubectl describe node node-1 | grep -i Taints
The flag -i is used to perform a case-insensitive search for the term "Taints". Just in case you don't know how it is capitalized.
Use ConfigMaps and Secrets to configure applications
- Create a ConfigMap called metal-cm containing the file
~/mycode/yaml/metal.html - To the deployment "enter-sandman" add the metal-cm ConfigMap mounted to the path
var/www/index.html - Create the deployment in the metallica namespace
kubectl create configmap metal-cm --from-file=~/mycode/yaml/metal.html -n metallica
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: enter-sandman
namespace: metallica
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: enter-sandman
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: enter-sandman
spec:
containers:
- name: web
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: metal-volume
mountPath: /var/www/index.html
volumes:
- name: metal-volume
configMap:
name: metal-cm
Use ConfigMaps and Secrets to configure applications
- You will adjust an existing pod named kiwi-secret-pod in namespace kiwi
- Make a new secret named juicysecret. It must contain the following key/value pairs:
- username=kiwis
- password=aredelicious
- Make this content available in the pod kiwi-secret-pod as environment variables USERKIWI and PASSKIWI
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: juicysecret
namespace: kiwi
type: Opaque
data:
username: kiwis
password: aredelicious
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: kiwi-secret-pod
namespace: kiwi
spec:
containers:
- name: kiwi-container
image: kiwi-image
env:
- name: USERKIWI
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: juicysecret
key: username
- name: PASSKIWI
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: juicysecret
key: password
Define and enforce Network Policies
- In namespace cherry you'll find two deployments named pit and stem. Both deployments are exposed via a service.
- Make a NetworkPolicy named cherry-control that:
- prevents outgoing traffic from the pit deployment
- Except to that of the stem deployment
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: cherry-control
namespace: cherry
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: pit
policyTypes:
- Ingress
- Egress
egress:
- to:
- podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: stem
Use Helm to install cluster components
- Modify the Helm chart configuration located at
~/ckad-helm-taskto ensure the deployment creates 3 replicas of a pod... - Then install the chart into the cluster
- The resources will be created in the battleofhelmsdeep namespace
Pretty simple, just setting the replica count in the values.yaml file to 3.
Rollback a deployment
- There is an existing deployment named mufasa in namespace king-of-lions
- Check the deployment history and rollback to a version that actually works
kubectl rollout history deployment mufasa -n king-of-lions
kubectl rollout undo deployment mufasa -n king-of-lions
kubeadm: Join a new node to the cluster
- Join node-2 to your existing kubeadm cluster. It has already been pre-provisioned with all necessary installations.
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
kubeadm join <control-plane-endpoint> --token <token> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:<hash>
The control-plane-endpoint is usually the IP address or hostname of the control plane node in your cluster. You can find it by running:
kubectl cluster-info
kubeadm: Upgrade an existing node
Look at kubeadm documentation, there are more steps.
kubeadm upgrade plan
kubeadm upgrade apply v1.32.1
Unresponsive Node Troubleshooting
If there is a node that is not ready:
kubectl describe node <node-name>
and there is no indication why this might be the case:
- SSH into the node
- Get the kubelet status:
sudo systemctl status kubelet - Check the kubelet logs:
sudo journalctl -u kubelet - Maybe just restart:
sudo systemctl restart kubelet
New Questions since February 2025
Storage
A developer needs a persistent volume for an application. Create a PersistentVolumeClaim with:
- size 100Mi
- access mode ReadWriteOnce
- using the storage-class "local-path"
Create a pod that mounts this PVC at /data and verify that the volume is automatically created and mounted.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: my-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Mi
storageClassName: local-path
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: my-container
image: my-image
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: my-pvc
volumes:
- name: my-pvc
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: my-pvc
Storage II
Create a StorageClass:
- named fast-storage
- uses the rancher.io/local-path provisioner
- sets a Retain reclaim policy
- uses Immediate binding (default)
Create a PersistentVolume and a PersistentVolumeClaim:
- the PV should use fast-storage
- configure node affinity so Kubernetes knows where to create the volume
- the PVC should bind to that PV
- Verify that when the PVC is deleted, the PV remains (in Released state)
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: fast-storage
provisioner: rancher.io/local-path
reclaimPolicy: Retain
volumeBindingMode: Immediate
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: my-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 100Mi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
storageClassName: fast-storage
claimRef:
namespace: default
name: my-pvc
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- my-node
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: my-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Mi
storageClassName: fast-storage
volumeName: my-pv
Storage III
Manually create a PersistentVolume that:
- is named static-pv-example
- requests 200Mi
- uses a hostPath on node-1
- access mode ReadWriteOnce
- Retain reclaim policy
Then create a matching PersistentVolumeClaim (static-pvc-example) to bind to it
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: static-pv-example
spec:
capacity:
storage: 200Mi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
hostPath:
path: /mnt/data
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- node-1
Node affinity docs: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/assign-pods-nodes-using-node-affinity/
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: static-pvc-example
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 200Mi
volumeName: static-pv-example
Autoscaling
Deploy a sample workload and configure Horizontal Pod Autoscaling for it. Specifically:
- Use the existing deployment
cpu-demo - Configure an HPA to scale this deployment from 1 up to 5 replicas when the average CPU utilization exceeds 50%.
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: cpu-demo-hpa
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: cpu-demo
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 5
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50
Node Affinity
Only schedule a Pod on the node that has a disktype=ssd label.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-pod
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: disktype
operator: In
values:
- ssd
containers:
- name: my-container
image: my-image
Pod Security
Enforce the Restricted Pod Security Standard on the namespace restricted-ns. Pods in that namespace cannot:
- have privileged access
- host networking
- have any elevated rights
=>> Page must be memorized... https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/enforce-standards-namespace-labels/
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: my-baseline-namespace
labels:
pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce: restricted
pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce-version: v1.33 # Not needed for this task
Taints and Tolerations
- On node node-1, add a taint so that no normal pods can schedule there.
- Then schedule a Pod on that node by adding the appropriate toleration to the Pod spec (and ensure it actually lands on node-2).
kubectl taint nodes node-1 key=value:NoSchedule
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-pod
spec:
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/hostname: node-1
tolerations:
- key: "key"
operator: "Equal"
value: "value"
effect: "NoSchedule"
containers:
- name: my-container
image: my-image
StatefulSets and Headless Services
- Deploy a StatefulSet named web with 2 replicas using the NGINX image.
- Each pod should have its own 1Gi persistent volume for /usr/share/nginx/html.
- Ensure that the StatefulSet pods have stable network identities and persistent storage that remains associated with the ordinal index (even if pods are rescheduled).
- Create a Headless Service named web to facilitate stable networking for the StatefulSet.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: web
labels:
app: web
spec:
clusterIP: None # Headless service
selector:
app: web # Select pods with the label app=web
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: web
spec:
serviceName: "web" # Must match the headless service name
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: web
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: web
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: www # Must match the volumeClaimTemplates name
volumeClaimTemplates: # Define a PVC template
- metadata:
name: www # Must match the volumeMount name
spec:
accessModes: ["ReadWriteOnce"]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
CoreDNS Troubleshooting
- Check the logs of the CoreDNS pods for any errors:
kubectl logs -n kube-system coredns-<id>- Configuration is inside a ConfigMap, to edit:
kubectl edit configmap coredns -n kube-system
- Configuration is inside a ConfigMap, to edit:
- Ensure that the CoreDNS service is correctly configured and running
- Verify that the DNS resolution is working for the pods by using tools like
nslookupordig.
CoreDNS Configuration
- Cluster workloads need to resolve a custom domain internally.
- Configure CoreDNS such that any DNS query for myapp.internal returns the IP address 10.10.10.10.
- After configuration, pods in the cluster should be able to resolve myapp.internal to 10.10.10.10.
Needed config:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: coredns
namespace: kube-system
data:
Corefile: |
.:53 {
errors
health
kubernetes cluster.local in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa {
pods insecure
fallthrough in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa
}
forward . /etc/resolv.conf
cache 30
loop
reload
loadbalance
}
hosts {
10.10.10.10 myapp.internal
fallthrough # Best practice to include
}
After that delete the coredns pod and it should automatically restart with the new configuration.
Test if it works:
kubectl run --rm -ti dns-client --image=busybox -- nslookup myapp.internal
Helm
- Use Helm to deploy the Traefik Ingress Controller on the cluster.
- Install it in a dedicated namespace traefik with release name traefik.
- Ensure that Traefik's support for the Kubernetes Gateway API is enabled via Helm values.
helm repo add traefik https://traefik.github.io/charts
helm repo update
helm install traefik traefik/traefik --namespace traefik --create-namespace --set experimental.kubernetesGateway.enabled=true
To get the values of the Helm chart (hopefully they will be provided):
helm show values traefik/traefik # grep is your friend if there is too much output
Kustomize
You have base manifests for an app in /home/student/kustomize/base. Use Kustomize to deploy a production variant of this app:
• The production variant should add the label environment: production to all resources.
• It should prefix resource names with prod-
• It should use Nginx image tag 1.21 instead of the base's 1.19
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eGv6iPWQKyo&t=2112s
Gateway API ("guaranteed task")
Your cluster uses the Gateway API for ingress traffic. A service named web-service is running in the default namespace on port 80. A Gateway API-compatible controller is already installed, and a GatewayClass named example-gw-class is available in the cluster.
Objective: Use Gateway API resources to expose web-service externally on HTTP port 80, routed via the hostname web.example.com.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: web-gateway
spec:
gatewayClassName: example-gw-class
listeners:
- name: http
protocol: HTTP
port: 80
hostname: web.example.com
allowedRoutes:
namespaces:
from: same
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: web-http-route
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: web-gateway
sectionName: http
hostnames:
- web.example.com
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: Prefix
value: /
backendRefs:
- name: web-service
port: 80
Pod Admission / Limit Ranges
In the namespace limit-test, enforce default resource limits and requests for containers:
- If a container has no CPU/memory requests/limits, assign a default request of 100m CPU and 50Mi memory, and a default limit of 200m CPU and 100Mi memory.
- Prevent any container in this namespace from requesting more than 500Mi memory.
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: limit-range
namespace: limit-test
spec:
limits:
- type: Container
default:
cpu: 200m
memory: 100Mi
defaultRequest:
cpu: 100m
memory: 50Mi
max:
memory: 500Mi
Important Notes
- https://www.reddit.com/r/devops/comments/1m1xj7q/comment/n3kpl0u/?share_id=luomAHCKTKEnrucnwBA0d&utm_medium=android_app&utm_name=androidcss&utm_source=share&utm_term=1
- VPAs are not covered only HPAs
- Installing packages with dpkg? How?
- Definitely look at CRDs
- Installing CRI?
- install calico cni
- update an immutable configmap
- argocd ==> add repo
- vim: use command
:syntax onfor syntax highlighting; :set paste + :set noai for inserting without issues - use kubectl explain
- Look at: https://github.com/anouarharrou/The-Ultimate-CKA-Guide/blob/main/My%20Note/CKA%20Simulations%20Exams%20Q&A.md
- I also highly recommend this resource: CKA Guide Q&A (Just one note: When installing Argo with HELM, you shouldn't use --skip-crds. Instead, set the appropriate Helm chart values.)
- Concerning strategy - I tackled the easier tasks first and flagged the difficult ones (troubleshooting) for later.
- Personally I recommend coming up with a list of docs pages you reference frequently when practicing and when you start the exam just open those pages up in the browser so you can quickly reference them if you need to. Example: for me, when I was studying I would frequently reference the K8s Documentation Pods page, the K8s API Reference Pods page, and the K8s Documentation Persistent Volume Page so when I started the exam the first thing I did was click the link to open up the K8s Documentation then duplicated that tab (right click tab -> duplicate) a couple times, then searched the docs for the appropriate pages in each one and had them open the whole exam. Its a small thing but it definitely helped knowing where they were and having them open so I didn't need to wait for loading or anything.
If ApiServer doesn't come up
Check logs, probably wrong configuration:
- Check
/var/log/kube-apiserver.log - Check
watch crictl ps -a|crictl logs <container-id>| Check/var/log/pods - Check
var/log/syslog - Edit
/etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-apiserver.yaml
If Kubelet has problems
- Check
/var/log/syslogorjournalctl - Check
journalctl -u kubelet | grep kubelet
If pods are pending and no errors
- Check if deployment specifies a specific node => remove it
Set node as unavailable for scheduling
Set the node named ek8s-node-0 as unavailable and reschedule all the pods running on it.
kubectl drain ek8s-node-0 --ignore-daemonsets --delete-emptydir-data # No need to remember --delete-emptydir-data flag (it will be mentioned by the CLI if necessary and not included)
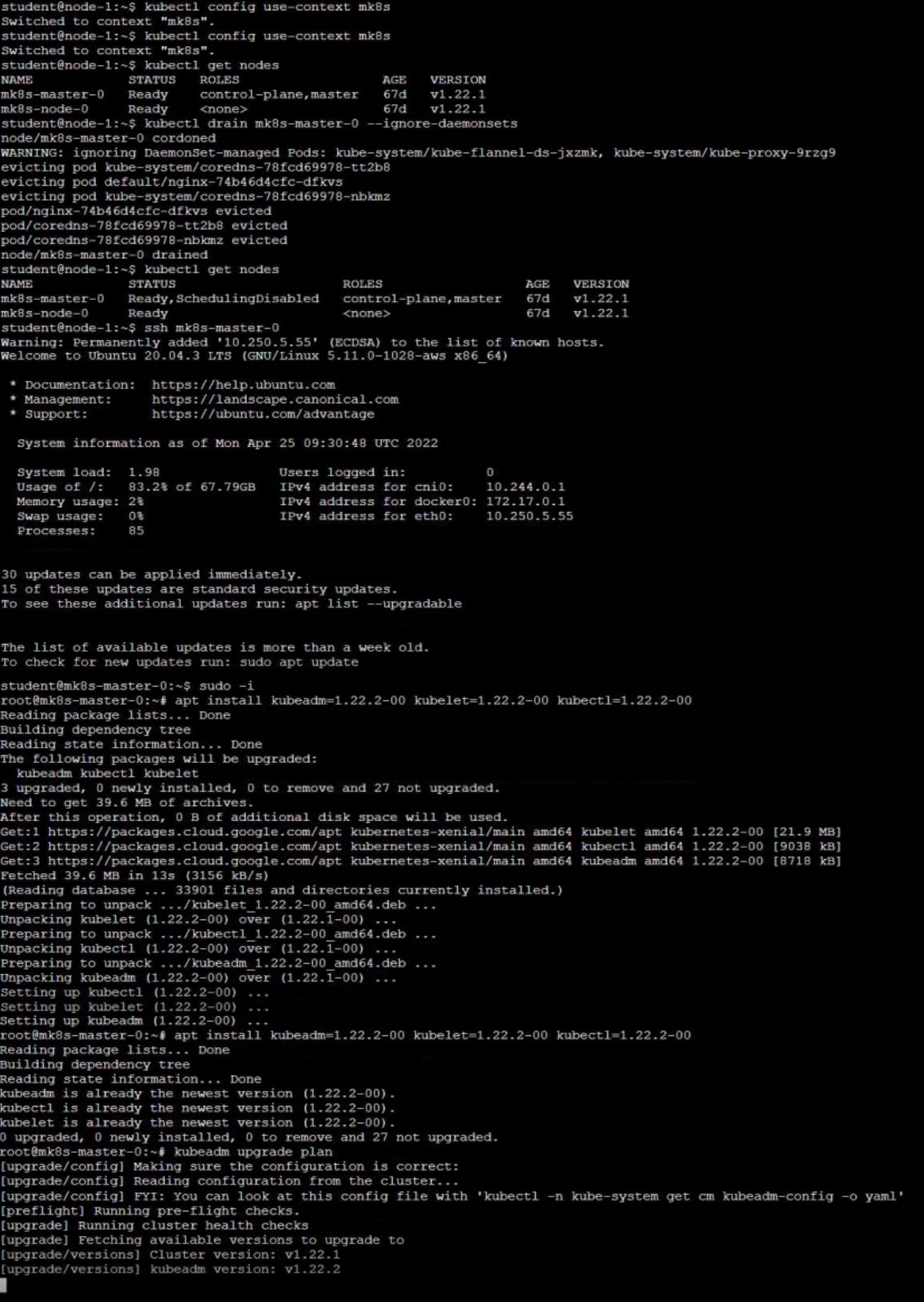
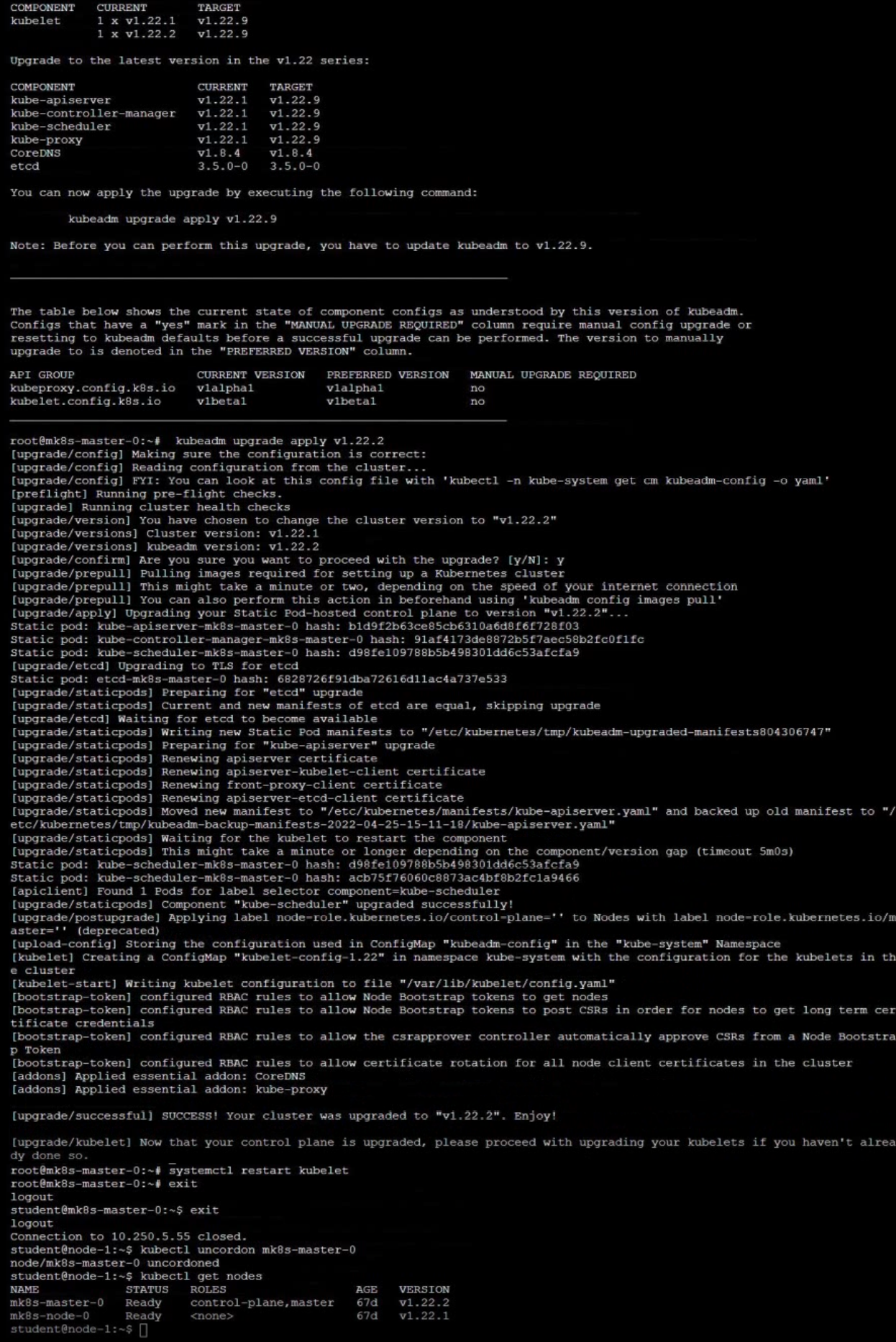
Upgrade Control Plane Node
Given an existing Kubernetes cluster running version 1.22.1, upgrade all of the Kubernetes control plane and node components on the master node only to version 1.22.2. Be sure to drain the master node before upgrading it and uncordon it after the upgrade.
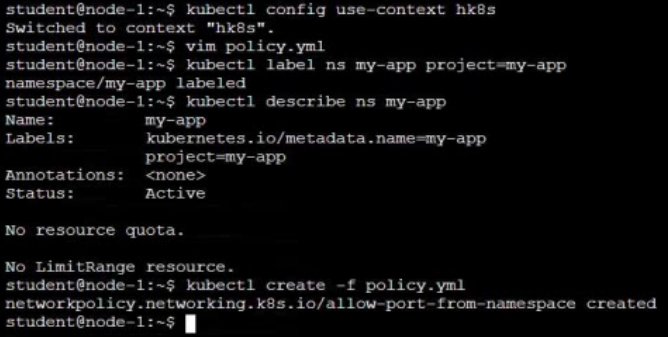
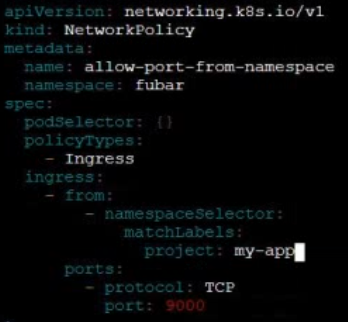
Network Policy
Create a new NetworkPolicy named allow-port-from-namespace in the existing namespace fubar. Ensure that the new NetworkPolicy allows Pods in namespace internal to connect to port 9000 of Pods in namespace fubar.
Further ensure that the new NetworkPolicy:
- does not allow access to Pods, which don't listen on port 9000
- does not allow access from Pods, which are not in namespace internal
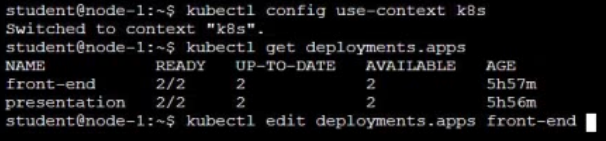
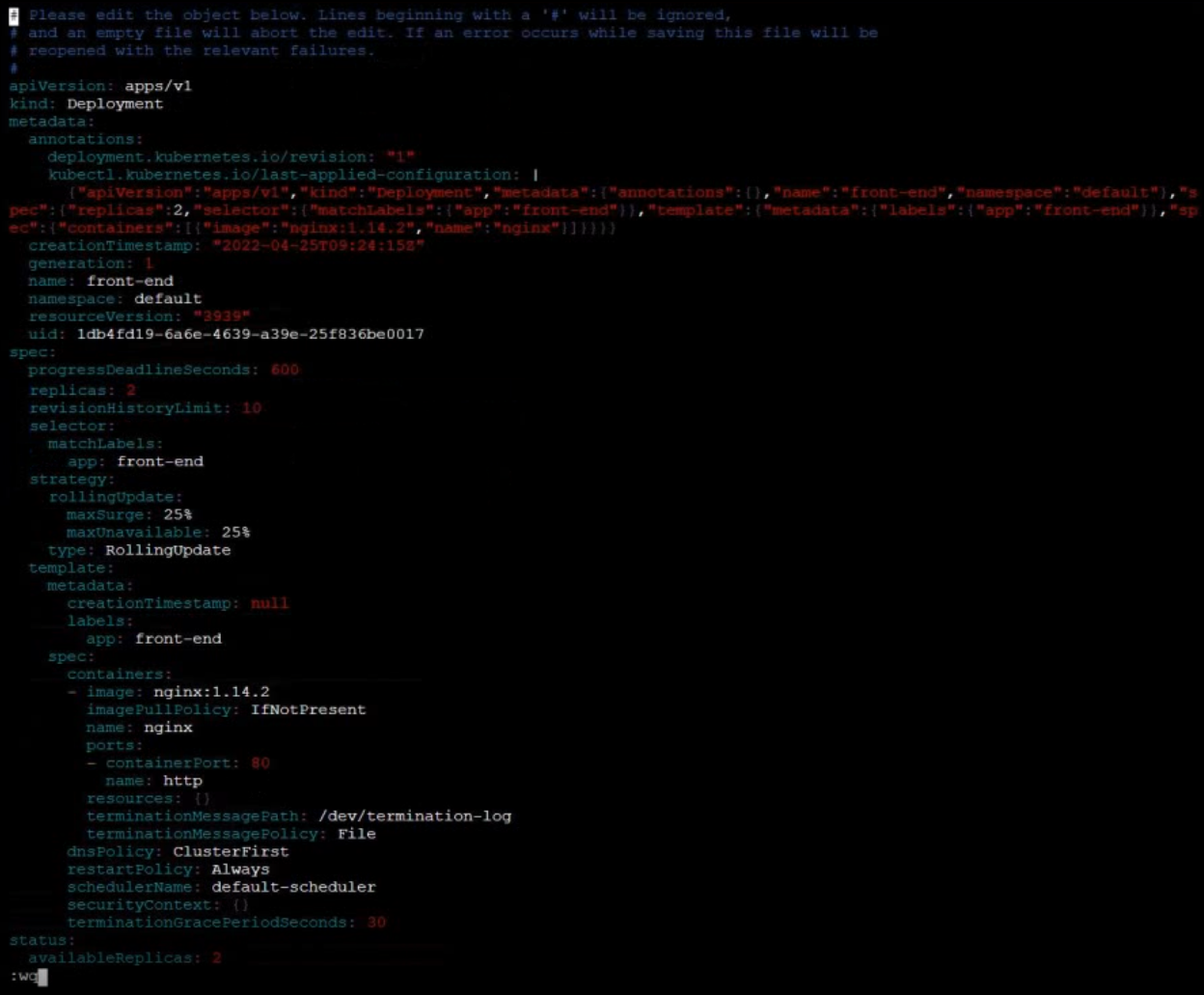
Reconfigure Deployment (add port)
- Reconfigure the existing deployment front-end and add a port specification named http exposing port 80/tcp of the existing container nginx.
- Create a new service named front-end-svc exposing the container port http.
- Configure the new service to also expose the individual Pods via a NodePort on the nodes on which they are scheduled.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-nodeport-service
spec:
type: NodePort # Specifies that this is a NodePort service
ports:
- port: 80 # Port exposed internally in the cluster
targetPort: 80 # Port your application is listening on in the Pod
nodePort: 30007 # Port exposed on each Node (must be between 30000-32767)
selector:
app: my-app # Must match the labels of the Pods you want to expose
Schedule a pod
Schedule a pod as follows:
- Name: nginx-kusc00401
- Image: nginx
- Node selector: disk=ssd
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-kusc00401
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
nodeSelector:
disk: ssd
PKI Essentials (kubeadm)
Directory: /etc/kubernetes/pki
- ca.crt: The public certificate for the cluster's Certificate Authority (CA).
- ca.key: The private key for the cluster's Certificate Authority (CA).
- apiserver.crt: The public certificate for the Kubernetes API server.
- apiserver.key: The private key for the Kubernetes API server.
- apiserver-kubelet-client.crt: The public certificate used by the API server to authenticate to kubelets.
- apiserver-kubelet-client.key: The private key used by the API server to authenticate to kubelets.
- front-proxy-ca.crt: The public certificate for the front proxy's Certificate Authority.
- front-proxy-ca.key: The private key for the front proxy's Certificate Authority.
- front-proxy-client.crt: The public certificate for the front proxy client.
- front-proxy-client.key: The private key for the front proxy client.
- etcd/ca.crt: The public certificate for the etcd cluster's Certificate Authority.
- etcd/ca.key: The private key for the etcd cluster's Certificate Authority.
- sa.pub: The public key for service account tokens.
- sa.key: The private key for service account tokens.
- apiserver-etcd-client.crt: The public certificate for the API server to communicate with etcd.
- etcd/server.crt: The public certificate for the etcd server.
- etcd/server.key: The private key for the etcd server.
- etcd/peer.crt: The public certificate for etcd peer communication.
- etcd/peer.key: The private key for etcd peer communication.
- etcd/healthcheck-client.crt: The public certificate for etcd health checks.
- etcd/healthcheck-client.key: The private key for etcd health checks.