Margin and Padding
Margin and Padding are the properties that are used to add space around the element.
- Margin is a distance from one package to another, it's an interblock space
- Padding refers to a shift from content to rim package
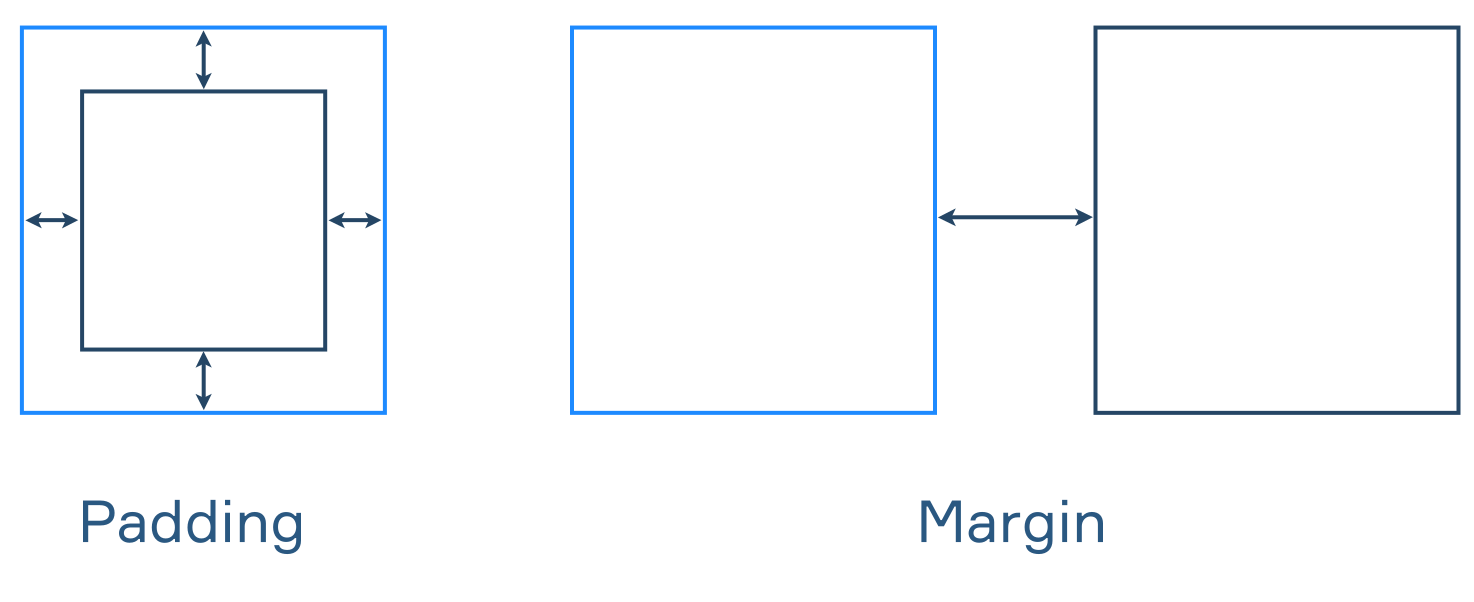
We therefore use margin for outside shifts and padding for inside shifts.
Properties
There are four properties for setting margins/padding for each side of the element: top, right, bottom, left. Definitions can be stated in any CSS unit (px, em, etc.).
For example: padding-right: 5%
Also, there is a contracted notation for margin and padding in CSS. It is possible to state one, two, three, or all four values at once:
- 4 values: top, right, bottom, left (e.g.
padding: 2px 5px 10px 5px) - 3 values: top, left/right, bottom (e.g.
padding: 2px 5px 10px) - 2 values: top/bottom, left/right (e.g.
padding: 2px 5px) - 1 value: top/right/bottom/left (e.g.
padding: 2px)
info
Negative values like margin-left: -5% are also possible.
Usage
Margin should be used when:
- You need to center an element. If that element has a fixed width, it will be centered horizontally by
margin: auto(will only work if the block width is set) - You need to make some content stand out by putting it separately without other elements touching it
Padding should be used when:
- You want to increase the size of the element. Padding will increase the size to accommodate the gap
- You need the element to have a background in the produced gap
- You need some space around the content