Constructable Stylesheets
Like HTML elements, CSS stylesheets can be created using JavaScript. The process has historically been to create a <style> element using document.createElement('style'), and then access its sheet property to obtain a reference to the underlying CSSStyleSheet instance. This method can produce duplicate CSS code and its attendant bloat, and the act of attaching leads to a flash of unstyled content whether there is bloat or not.
The CSSStyleSheet interface is the root of a collection of CSS representation interfaces referred to as the CSSOM, offering a programmatic way to manipulate stylesheets as well as eliminating the problems associated with the old method.
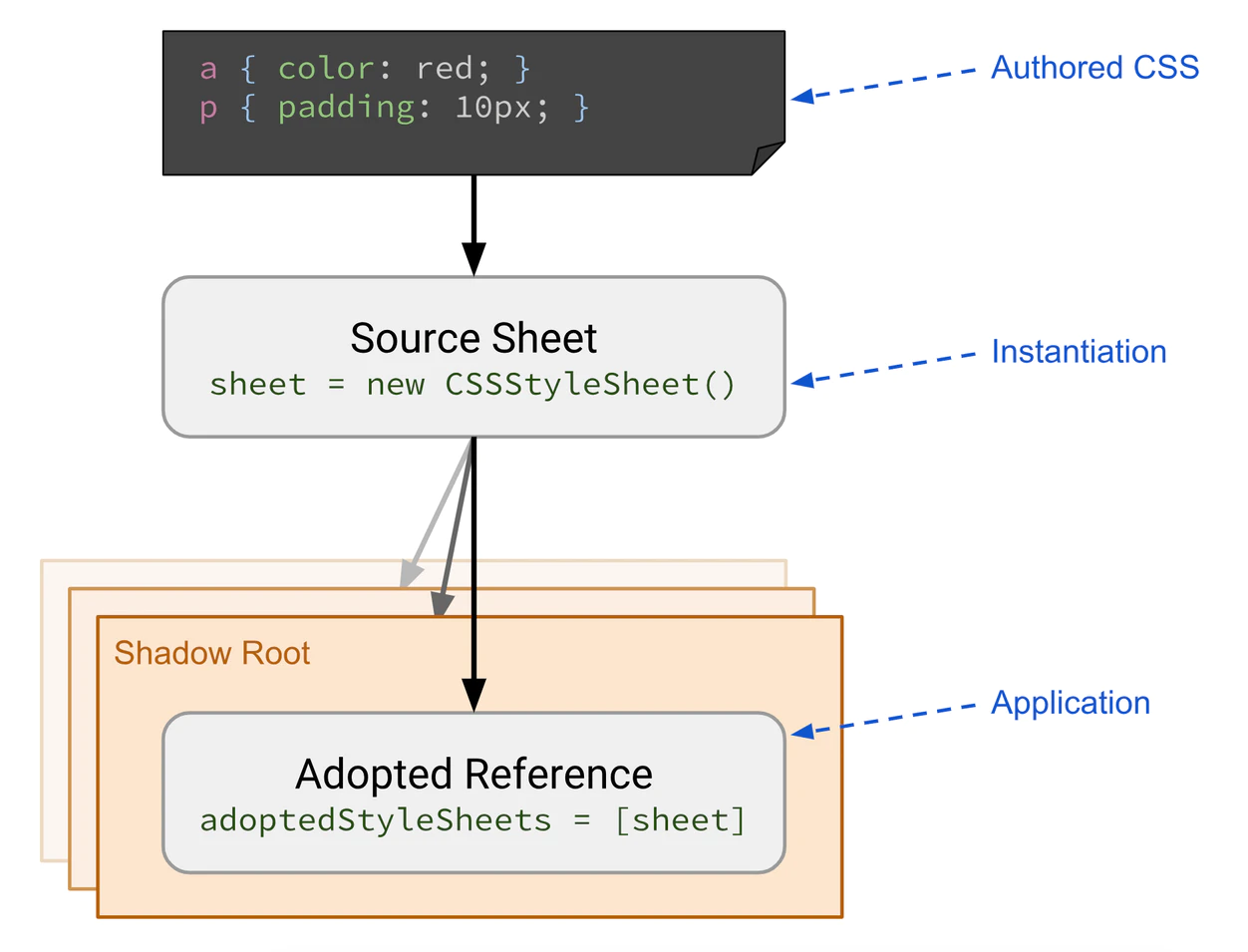
Constructable Stylesheets make it possible to define and prepare shared CSS styles, and then apply those styles to multiple Shadow Roots or the Document easily and without duplication. Updates to a shared CSSStyleSheet are applied to all roots into which it has been adopted, and adopting a stylesheet is fast and synchronous once the sheet has been loaded.
Usage
Constructable Stylesheets can be used:
- to provide a centralized theme used by many components
- the theme can be a
CSSStyleSheetinstance passed to components, with updates to the theme propagating out to components automatically
- the theme can be a
- to distribute CSS Custom Property values to specific DOM subtrees without relying on the cascade
- as a direct interface to the browser's CSS parser, making it easy to preload stylesheets without injecting them into the DOM
Constructing a stylesheet
The Constructable StyleSheets specification makes it possible to create stylesheets imperatively by invoking the CSSStyleSheet() constructor. The resulting CSSStyleSheet object has two new methods that make it safer to add and update stylesheet rules without triggering Flash of Unstyled Content (FOUC). The replace() and replaceSync() methods both replace the stylesheet with a string of CSS, and replace() returns a Promise.