Advanced Identity
AWS STS – Security Token Service
- Allows to grant limited and temporary access to AWS resources (up to 1 hour).
- AssumeRole: Assume roles within your account or cross account
- AssumeRoleWithSAML: return credentials for users logged with SAML
- AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity
- return creds for users logged with an IdP (Facebook Login, Google Login, OIDC compatible…)
- AWS recommends against using this, and using Cognito Identity Pools instead
- GetSessionToken: for MFA, from a user or AWS account root user
- GetFederationToken: obtain temporary creds for a federated user
- GetCallerIdentity: return details about the IAM user or role used in the API call
- DecodeAuthorizationMessage: decode error message when an AWS API is denied
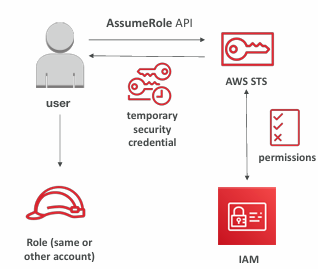
Using STS to Assume a Role
- Define an IAM Role within your account or cross-account
- Define which principals can access this IAM Role
- Use AWS STS (Security Token Service) to retrieve credentials and impersonate the IAM Role you have access to (AssumeRole API)
- Temporary credentials can be valid between 15 minutes to 1 hour
Cross account access with STS
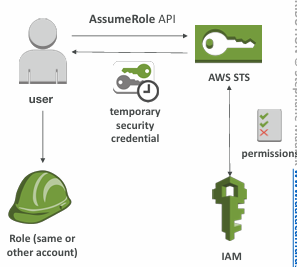
STS with MFA
- Use GetSessionToken from STS
- Appropriate IAM policy using IAM Conditions
- aws:MultiFactorAuthPresent:true
- Reminder, GetSessionToken returns:
- Access ID
- Secret Key
- Session Token
- Expiration date
IAM Best Practices
General
- Never use Root Credentials, enable MFA for Root Account
- Grant Least Privilege
- Each Group / User / Role should only have the minimum level of permission it needs
- Never grant a policy with “*” access to a service
- Monitor API calls made by a user in CloudTrail (especially Denied ones)
- Never ever ever store IAM key credentials on any machine but a personal computer or on-premise server
- On premise server best practice is to call STS to obtain temporary security credentials
IAM Roles
- EC2 machines should have their own roles
- Lambda functions should have their own roles
- ECS Tasks should have their own roles (ECS_ENABLE_TASK_IAM_ROLE=true)
- CodeBuild should have its own service role
- Create a least-privileged role for any service that requires it
- Create a role per application / lambda function (do not reuse roles)
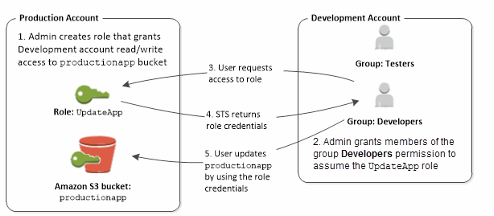
Cross Account Access
- Define an IAM Role for another account to access
- Define which accounts can access this IAM Role
- Use AWS STS (Security Token Service) to retrieve credentials and impersonate the IAM Role you have access to (AssumeRole API)
- Temporary credentials can be valid between 15 minutes to 1 hour
Authorization Model Evaluation of Policies
- If there’s an explicit DENY, end decision and DENY
- If there’s an ALLOW, end decision with ALLOW
- Else DENY
IAM Policies & S3 Bucket Policies
- IAM Policies are attached to users, roles, groups
- S3 Bucket Policies are attached to buckets
- When evaluating if an IAM Principal can perform an operation X on a bucket, the union of its assigned IAM Policies and S3 Bucket policies will be evaluated.
Example 1
- IAM Role attached to EC2 instance, authorizes RW to “my_bucket”
- No S3 Bucket Policy attached
- => EC2 instance can read and write to “my_bucket”
Example 2
- IAM Role attached to EC2 instance, authorizes RW to “my_bucket”
- S3 Bucket Policy attached, explicit deny
- => EC2 instance cannot to the IAM Role read and write to “my_bucket”
Example 3
- IAM Role attached to EC2 instance, no S3 bucket permissions
- S3 Bucket Policy attached, explicit RW allow
- => EC2 instance can to the IAM Role read and write to “my_bucket”
Example 4
- IAM Role attached to EC2 instance, explicit deny S3 bucket permissions
- S3 Bucket Policy attached, explicit RW allow
- => EC2 instance cannot to the IAM Role read and write to “my_bucket”
Dynamic Policies with IAM
How do you assign each user a /home/<user> folder in an S3 bucket?
- Option 1:
- Create an IAM policy allowing georges to have access to /home/georges
- Create an IAM policy allowing sarah to have access to /home/sarah
- Create an IAM policy allowing matt to have access to /home/matt
- … One policy per user!
- This doesn’t scale
- Option 2:
- Create one dynamic policy with IAM
- Leverage the special policy variable
${aws:username}
{
"Sid": "AllowAllS3ActionsInUserFolder",
"Action": ["s3:*"],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": ["arn:aws:s3:::my-company/home/${aws:username}/*"]
}
Inline vs Managed Policies
- AWS Managed Policy
- Maintained by AWS
- Good for power users and administrators
- Updated in case of new services / new APIs
- Customer Managed Policy
- Best Practice, re-usable, can be applied to many principals
- Version Controlled + rollback, central change management
- Inline
- Strict one-to-one relationship between policy and principal
- Policy is deleted if you delete the IAM principal
Granting a User Permissions to Pass a Role to an AWS Service
- To configure many AWS services, you must pass an IAM role to the service (this happens only once during setup)
- The service will later assume the role and perform actions
- Example of passing a role:
- To an EC2 instance
- To a Lambda function
- To an ECS task
- To CodePipeline to allow it to invoke other services
- For this, you need the IAM permission iam:PassRole
- It often comes with iam:GetRole to view the role being passed

- Roles can only be passed to what their trust allows
- A trust policy for the role that allows the service to assume the role

What is Microsoft Active Directory (AD)?
- Found on any Windows Server with AD Domain Services
- Database of objects: User Accounts, Computers, Printers, File Shares, Security Groups
- Centralized security management, create account, assign permissions
- Objects are organized in trees
- A group of trees is a forest
AWS Directory Services
- AWS Managed Microsoft AD
- Create your own AD in AWS, manage users locally, supports MFA
- Establish “trust” connections with your on premise AD
- AD Connector
- Directory Gateway (proxy) to redirect to on premise AD, supports MFA
- Users are managed on the on-premise AD
- Simple AD
- AD-compatible managed directory on AWS
- Cannot be joined with on-premise AD