Cognito
- Give users an identity to interact with our web or mobile application
- Cognito User Pools:
- Sign in functionality for app users
- Integrate with API Gateway & Application Load Balancer
- Cognito Identity Pools (Federated Identity):
- Provide AWS credentials to users so they can access AWS resources directly
- Integrate with Cognito User Pools as an identity provider
- Cognito vs IAM: “hundreds of users”, ”mobile users”, “authenticate with SAML”
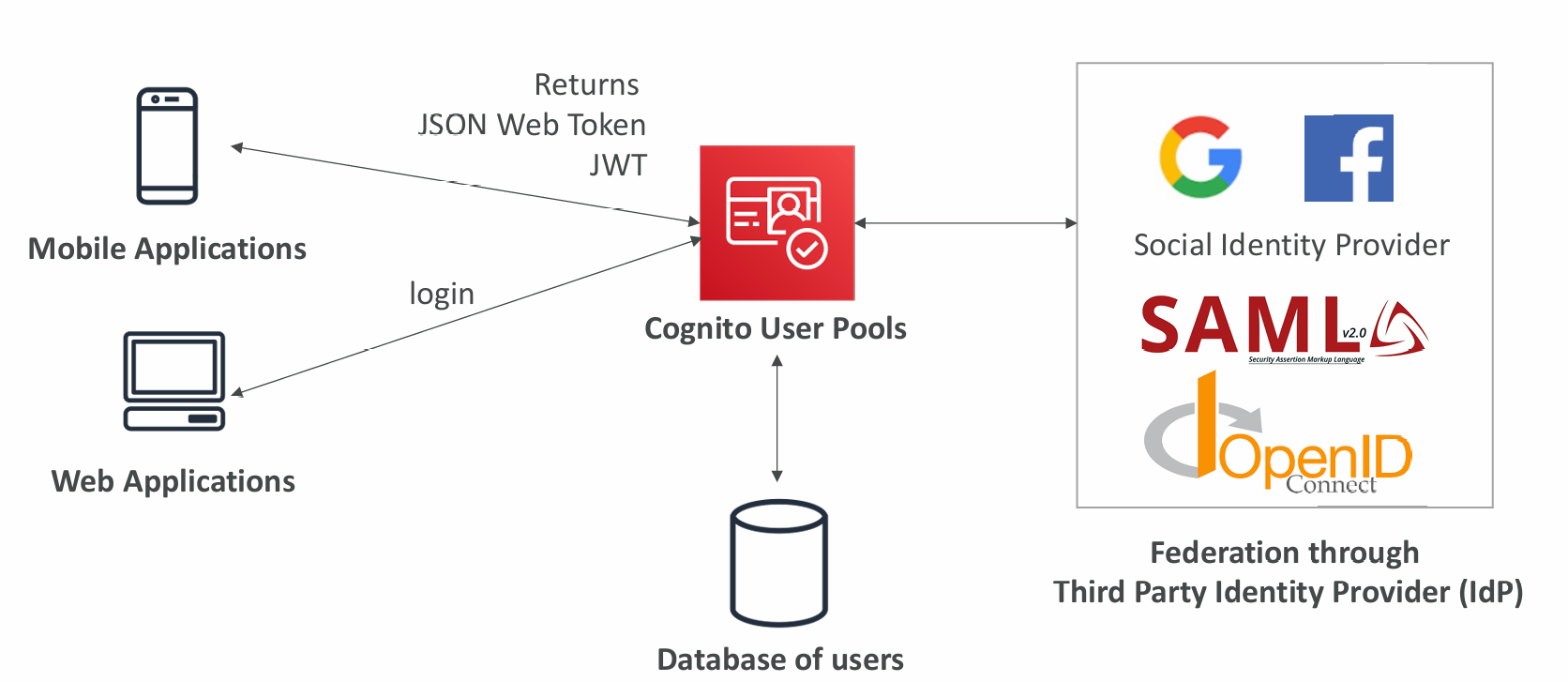
Cognito User Pools (CUP) – User Features
- Create a serverless database of user for your web & mobile apps
- Simple login: Username (or email) / password combination
- Password reset
- Email & Phone Number Verification
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Federated Identities: users from Facebook, Google, SAML…
- Feature: block users if their credentials are compromised elsewhere
- Login sends back a JSON Web Token (JWT)
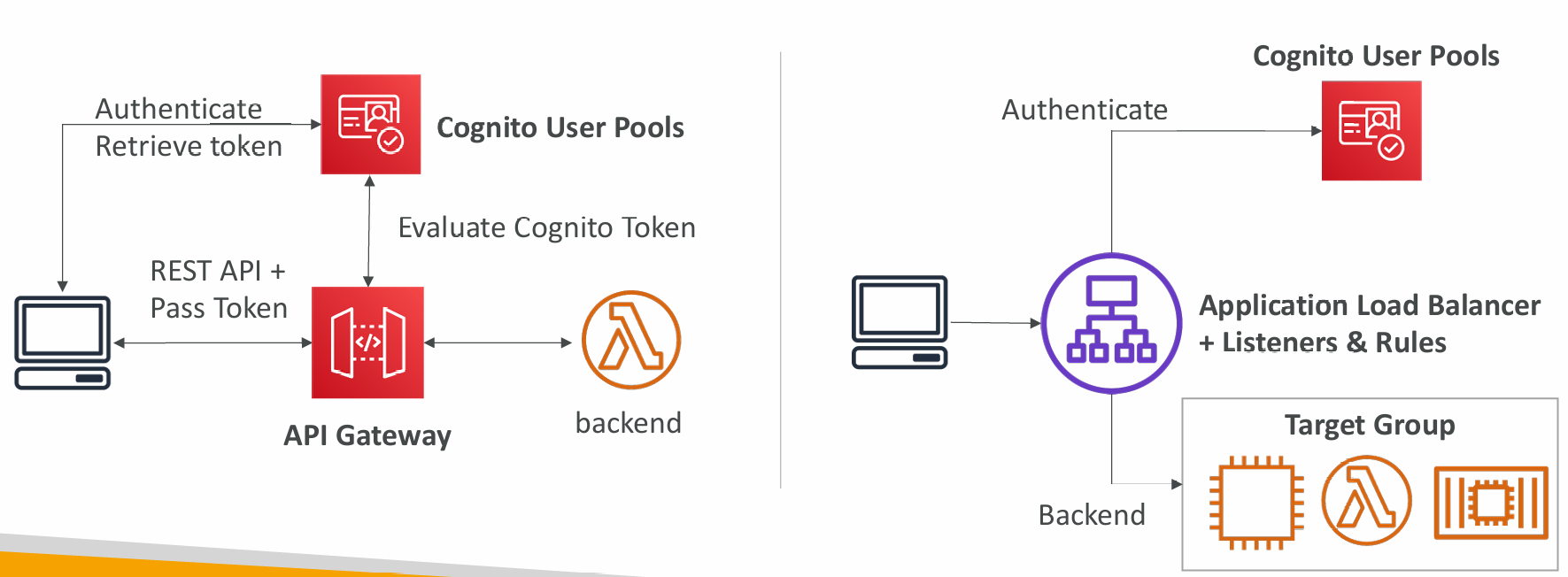
Integrations
CUP integrates with API Gateway and Application Load Balancer:
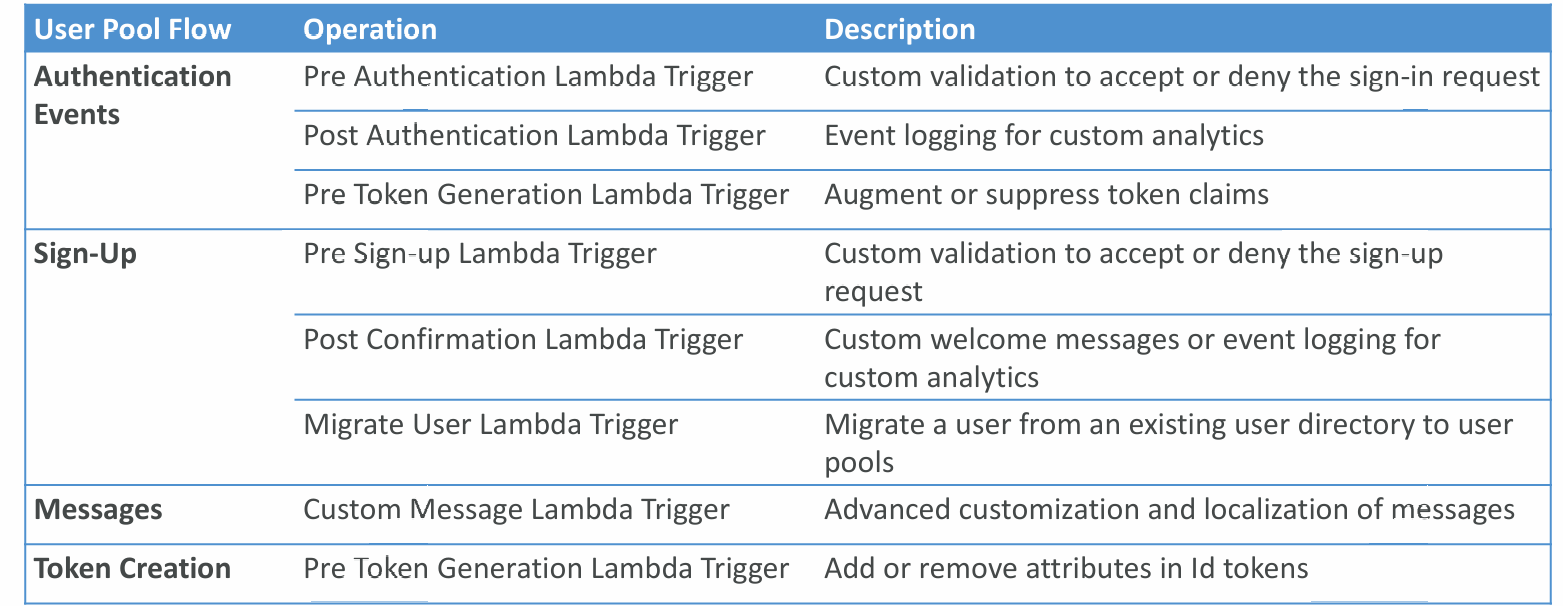
Lambda Triggers
CUP can invoke a Lambda function synchronously on these triggers:
Hosted Authentication UI
- Cognito has a hosted authentication UI that you can add to your app to handle sign-up and sign-in workflows
- Using the hosted UI, you have a foundation for integration with social logins, OIDC or SAML
- Can customize with a custom logo and custom CSS
Hosted UI Custom Domain
- For custom domains, you must create an ACM certificate in us-east-1
- The custom domain must be defined in the “App Integration” section
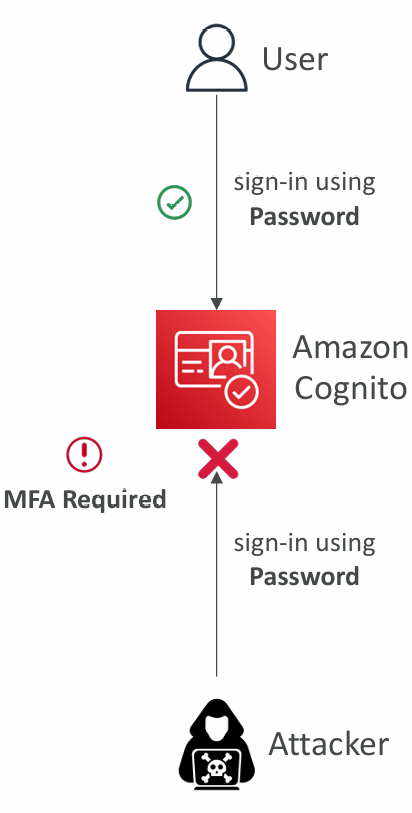
Adaptive Authentication
- Block sign-ins or require MFA if the login appears suspicious
- Cognito examines each sign-in attempt and generates a risk score (low, medium, high) for how likely the sign-in request is to be from a malicious attacker
- Users are prompted for a second MFA only when risk is detected
- Risk score is based on different factors such as if the user has used the same device, location, or IP address
- Checks for compromised credentials, account takeover protection, and phone and email verification
- Integration with CloudWatch Logs (sign-in attempts, risk score, failed challenges…)
Decoding a ID Token; JWT – JSON Web Token
- CUP issues JWT tokens (Base64 encoded):
- Header
- Payload
- Signature
- The signature must be verified to ensure the JWT can be trusted
- Libraries can help you verify the validity of JWT tokens issued by Cognito User Pools
- The Payload will contain the user information (sub UUID, given_name, email, phone_number, attributes…)
- From the sub UUID, you can retrieve all users details from Cognito / OIDC

Application Load Balancer – Authenticate Users
- Your Application Load Balancer can securely authenticate users
- Offload the work of authenticating users to your load balancer
- Your applications can focus on their business logic
- Authenticate users through:
- Identity Provider (IdP): OpenID Connect (OIDC) compliant
- Cognito User Pools:
- Social IdPs, such as Amazon, Facebook, or Google
- Corporate identities using SAML, LDAP, or Microsoft AD
- Must use an HTTPS listener to set authenticate-oidc & authenticate-cognito rules
- OnUnauthenticatedRequest – authenticate (default), deny, allow
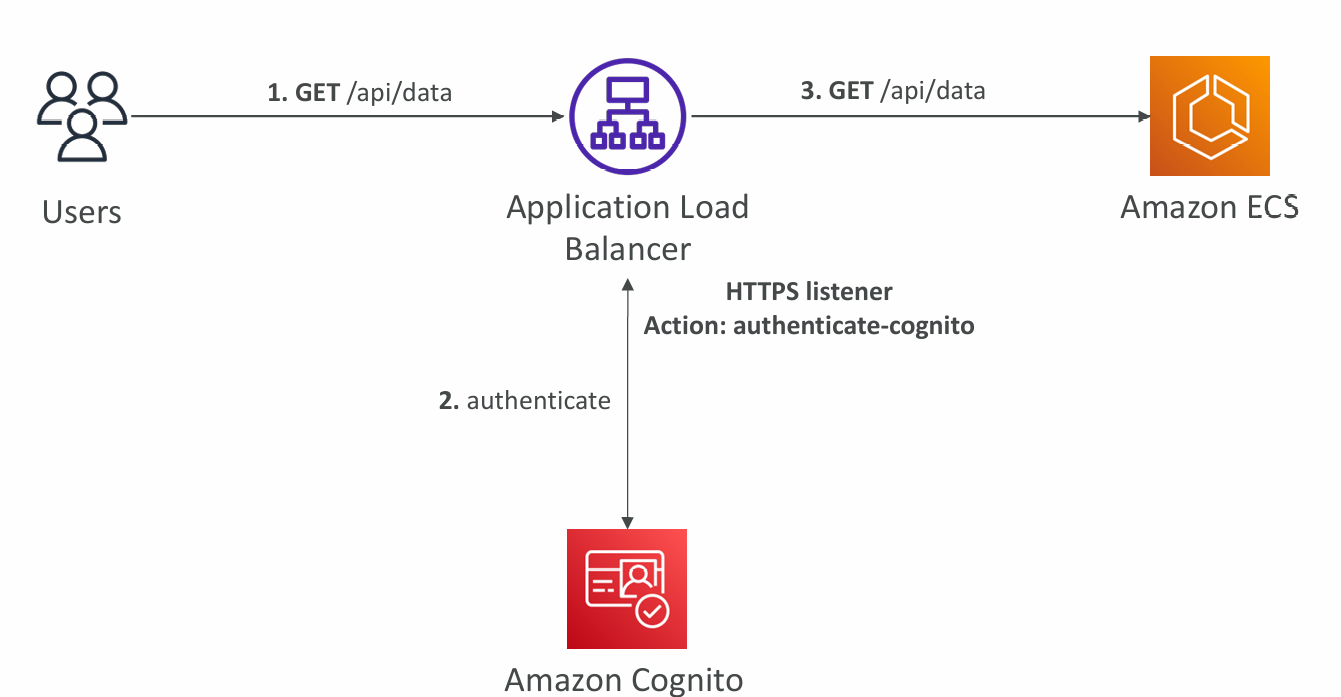
Auth through Cognito User Pools
- Create Cognito User Pool, Client and Domain
- Make sure an ID token is returned
- Add the social or Corporate IdP if needed
- Several URL redirections are necessary
- Allow your Cognito User Pool Domain on your IdP app's callback URL. For example:
OIDC Authentication
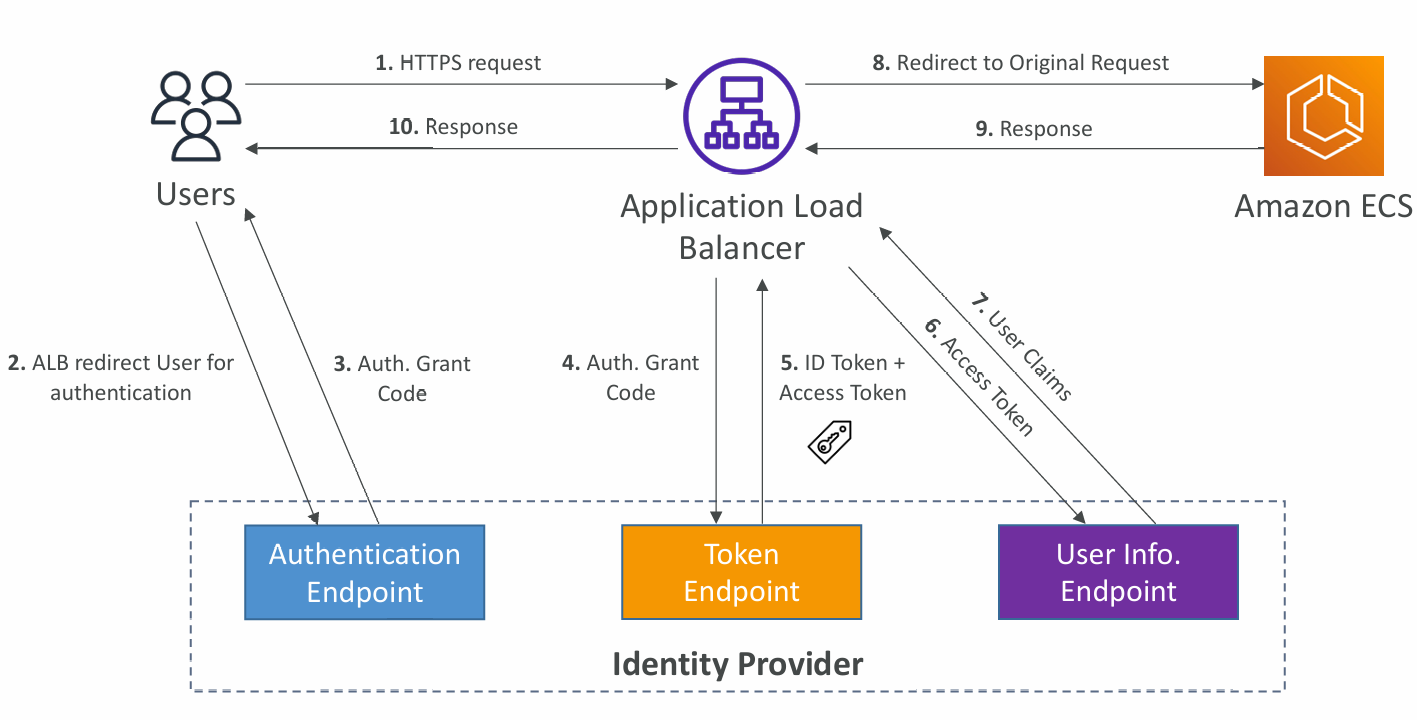
Auth. Through an Identity Provider (IdP) - OIDC compliant
- Configure a Client ID & Client Secret
- Allow redirect from OIDC to your Application Load Balancer DNS name (AWS provided) and CNAME (DNS Alias of your app)
Cognito Identity Pools (Federated Identities)
- Get identities for “users” so they obtain temporary AWS credentials
- Your identity pool (e.g identity source) can include:
- Public Providers (Login with Amazon, Facebook, Google, Apple)
- Users in an Amazon Cognito user pool
- OpenID Connect Providers & SAML Identity Providers
- Developer Authenticated Identities (custom login server)
- Cognito Identity Pools allow for unauthenticated (guest) access
- Users can then access AWS services directly or through API Gateway
- The IAM policies applied to the credentials are defined in Cognito
- They can be customized based on the user_id for fine grained control
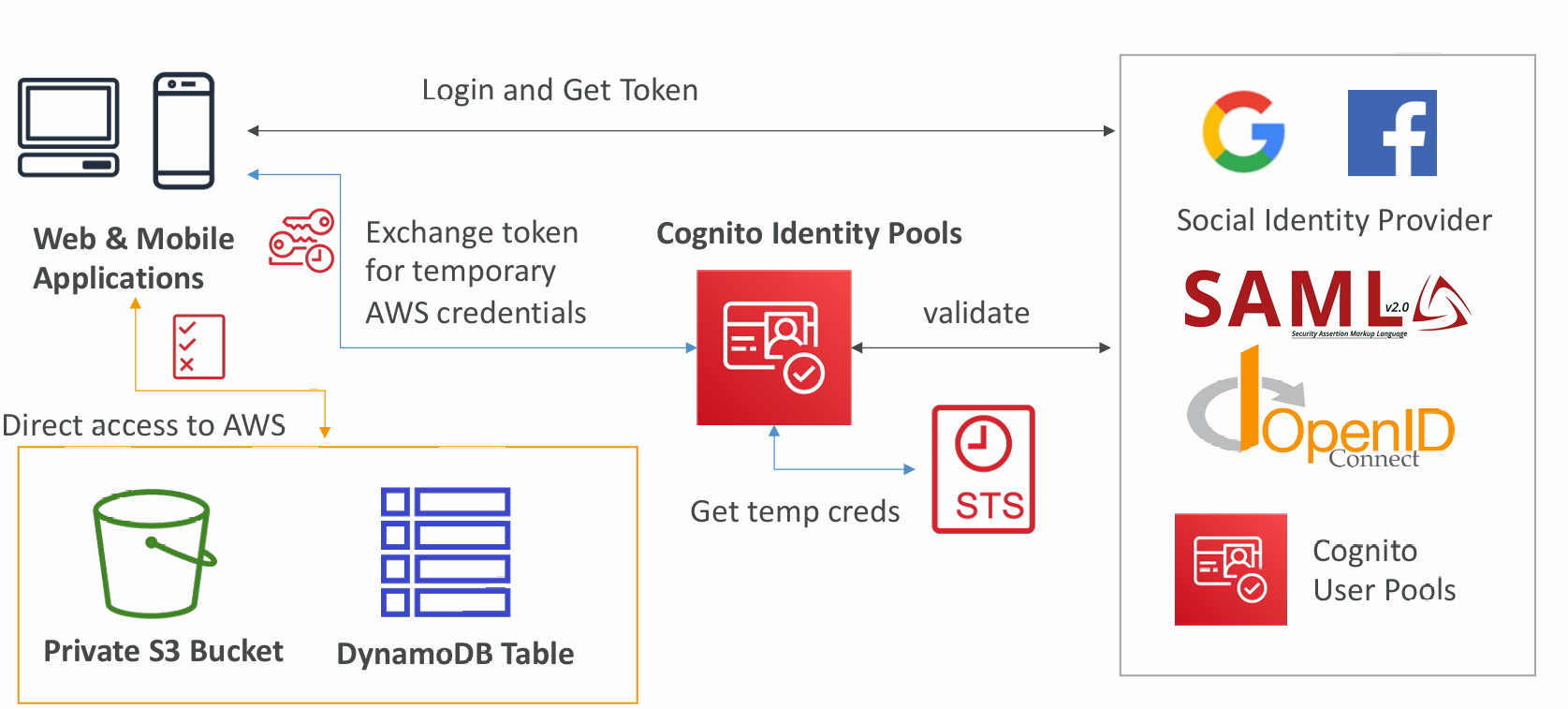
With CUP:
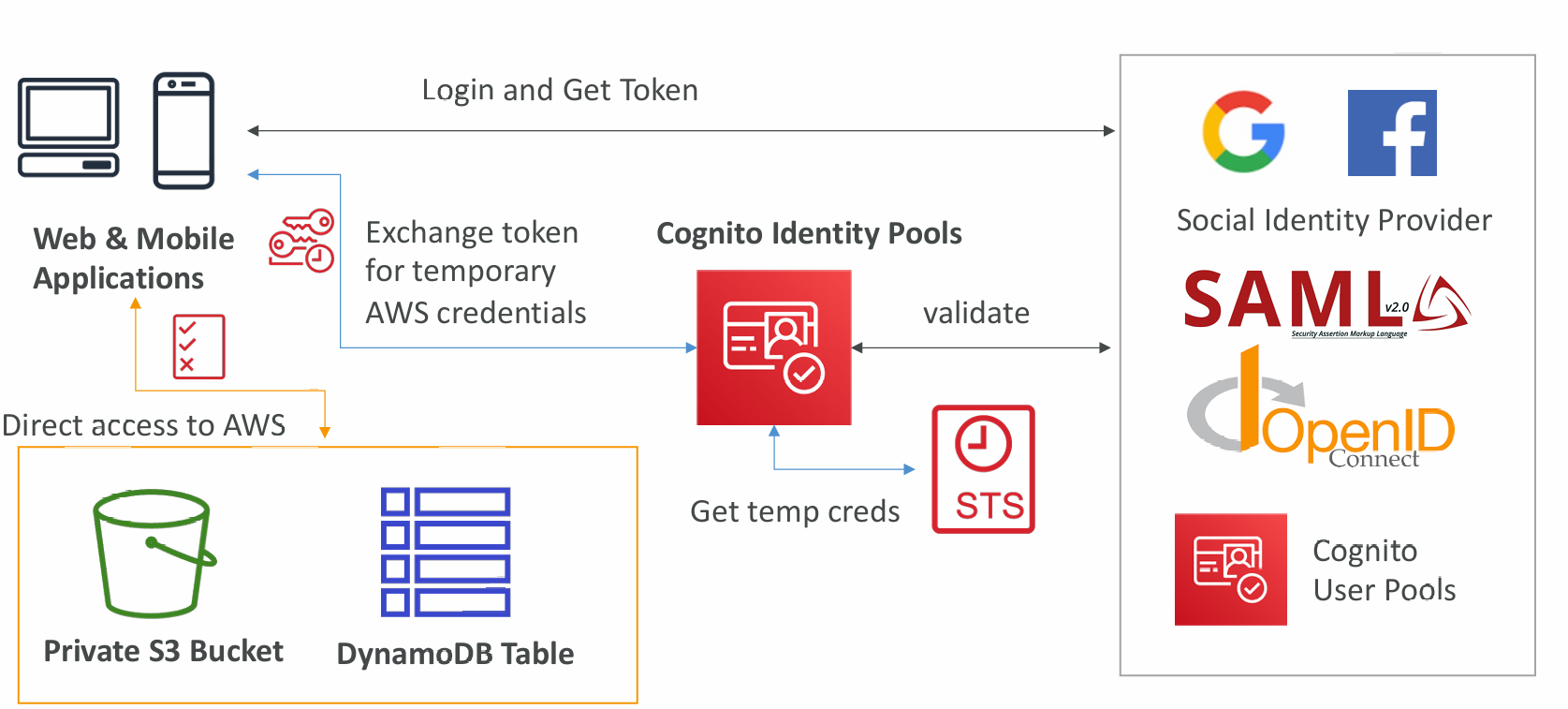
IAM Roles
- Default IAM roles for authenticated and guest users
- Define rules to choose the role for each user based on the user’s ID
- You can par tition your users’ access using policy variables
- IAM credentials are obtained by Cognito Identity Pools through STS
- The roles must have a “trust” policy of Cognito Identity Pools
Guest User example

Policy variable on S3

DynamoDB

Cognito User Pools vs Identity Pools
- Cognito User Pools (for authentication = identity verification)
- Database of users for your web and mobile application
- Allows to federate logins through Public Social, OIDC, SAML…
- Can customize the hosted UI for authentication (including the logo)
- Has triggers with AWS Lambda during the authentication flow
- Adapt the sign-in experience to different risk levels (MFA, adaptive authentication, etc…)
- Cognito Identity Pools (for authorization = access control)
- Obtain AWS credentials for your users
- Users can login through Public Social, OIDC, SAML & Cognito User Pools
- Users can be unauthenticated (guests)
- Users are mapped to IAM roles & policies, can leverage policy variables
- CUP + CIP = authentication + authorization