Security & Encryption
AWS KMS (Key Management Service)
- Anytime you hear “encryption” for an AWS service, it’s most likely KMS
- AWS manages encryption keys for us
- Fully integrated with IAM for authorization
- Easy way to control access to your data
- Able to audit KMS Key usage using CloudTrail
- Seamlessly integrated into most AWS services (EBS, S3, RDS, SSM…)
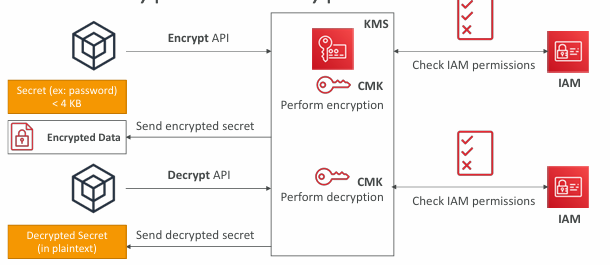
- Never ever store your secrets in plaintext, especially in your code!
- KMS Key Encryption also available through API calls (SDK, CLI)
- Encrypted secrets can be stored in the code / environment variables
KMS Keys Types
- KMS Keys is the new name of KMS Customer Master Key
- Symmetric (AES-256 keys)
- Single encryption key that is used to Encrypt and Decrypt
- AWS services that are integrated with KMS use Symmetric CMKs
- You never get access to the KMS Key unencr ypted (must call KMS API to use)
- Asymmetric (RSA & ECC key pairs)
- Public (Encrypt) and Private Key (Decrypt) pair
- Used for Encrypt/Decrypt, or Sign/Verify operations
- The public key is downloadable, but you can’t access the Private Key unencrypted
- Use case: encryption outside of AWS by users who can’t call the KMS API
- Types of KMS Keys:
- AWS Owned Keys (free): SSE-S3, SSE-SQS, SSE-DDB (default key)
- AWS Managed Key: free (aws/service-name, example: aws/rds or aws/ebs)
- Customer managed keys created in KMS: $1 / month
- Customer managed keys imported: $1 / month
- pay for API call to KMS ($0.03 / 10000 calls)
- Automatic Key rotation:
- AWS-managed KMS Key: automatic every 1 year
- Customer-managed KMS Key: (must be enabled) automatic & on-demand
- Imported KMS Key: only manual rotation possible using alias
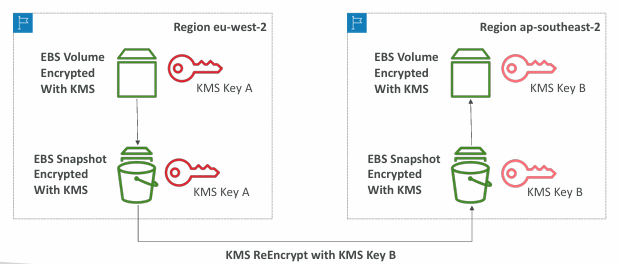
Copying Snapshots across regions
KMS Key Policies
- Control access to KMS keys, “similar” to S3 bucket policies
- Difference: you cannot control access without them
- Default KMS Key Policy:
- Created if you don’t provide a specific KMS Key Policy
- Complete access to the key to the root user = entire AWS account
- Custom KMS Key Policy:
- Define users, roles that can access the KMS key
- Define who can administer the key
- Useful for cross-account access of your KMS key
Copying Snapshots across accounts
- Create a Snapshot, encrypted with your own KMS Key (Customer Managed Key)
- Attach a KMS Key Policy to authorize cross-account access
- Share the encrypted snapshot
- (in target) Create a copy of the Snapshot, encrypt it with a CMK in your account
- Create a volume from the snapshot
KMS API - Encrypt and Decrypt
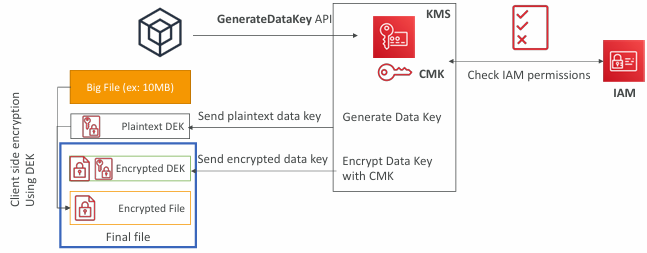
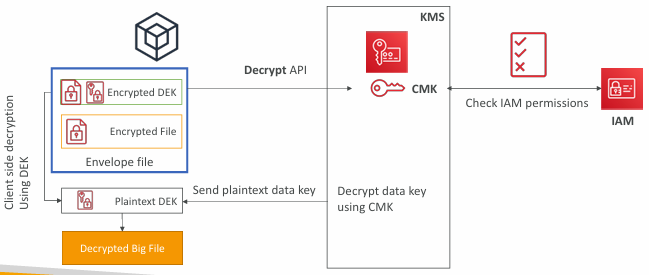
Envelope Encryption
- KMS Encrypt API call has a limit of 4 KB
- If you want to encrypt >4 KB, we need to use Envelope Encryption
- The main API that will help us is the GenerateDataKey API
- For the exam: anything over 4 KB of data that needs to be encrypted must use the Envelope Encryption == GenerateDataKey API
GenerateDataKey API
Decrypt envelope data
Encryption SDK
- The AWS Encryption SDK implemented Envelope Encryption for us
- The Encryption SDK also exists as a CLI tool we can install
- Implementations for Java, Python, C, JavaScript
- Feature - Data Key Caching:
- re-use data keys instead of creating new ones for each encryption
- Helps with reducing the number of calls to KMS with a security trade-off
- Use LocalCryptoMaterialsCache (max age, max bytes, max number of messages)
- The SDK encrypts the data encryption key and stores it (encrypted) as part of the returned ciphertext.
KMS Symmetric – API Summary
- Encrypt: encrypt up to 4 KB of data through KMS
- GenerateDataKey: generates a unique symmetric data key (DEK)
- returns a plaintext copy of the data key
- AND a copy that is encrypted under the CMK that you specify
- GenerateDataKeyWithoutPlaintext:
- Generate a DEK to use at some point (not immediately)
- DEK that is encrypted under the CMK that you specify (must use Decrypt later)
- Decrypt: decrypt up to 4 KB of data (including Data Encryption Keys)
- GenerateRandom: Returns a random byte string
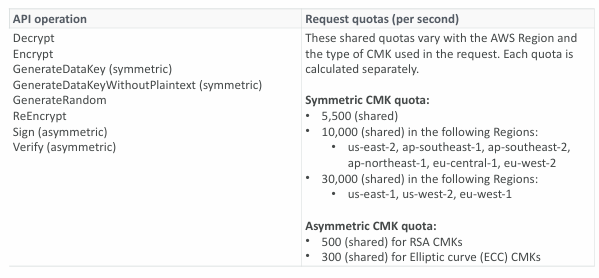
KMS Request Quotas
- When you exceed a request quota, you get a ThrottlingException
- To respond, use exponential backoff (backoff and retry)
- For cryptographic operations, they share a quota
- This includes requests made by AWS on your behalf (ex: SSE-KMS)
- For GenerateDataKey, consider using DEK caching from the Encryption SDK
- You can request a Request Quotas increase through API or AWS support
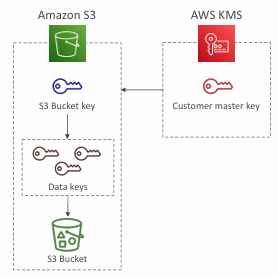
S3 Bucket Key for SSE-KMS encryption
- New setting to decrease…
- Number of API calls made to KMS from S3 by 99%
- Costs of overall KMS encryption with Amazon S3 by 99%
- This leverages data keys
- A “S3 bucket key” is generated
- That key is used to encrypt KMS objects with new data keys
- You will see less KMS CloudTrail events in CloudTrail
Key Policy – Examples

Principal Options in IAM Policies


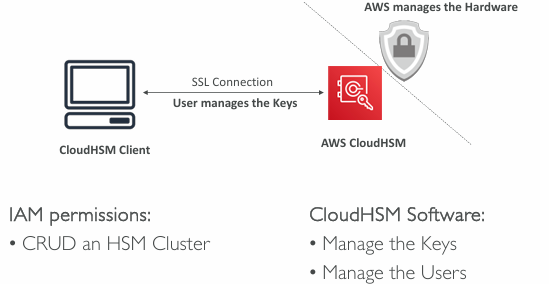
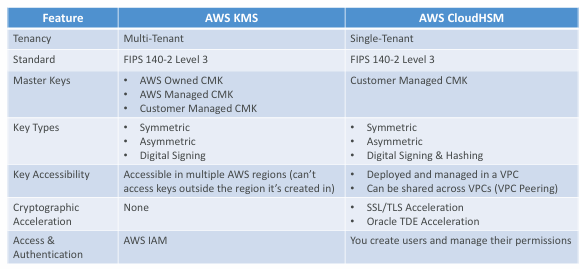
CloudHSM
- KMS => AWS manages the software for encryption
- CloudHSM => AWS provisions encryption hardware
- Dedicated Hardware (HSM = Hardware Security Module)
- You manage your own encryption keys entirely (not AWS)
- HSM device is tamper resistant, FIPS 140-2 Level 3 compliance
- Supports both symmetric and asymmetric encryption (SSL/TLS keys)
- No free tier available
- Must use the CloudHSM Client Software
- Redshift supports CloudHSM for database encryption and key management
- Good option to use with SSE-C encryption
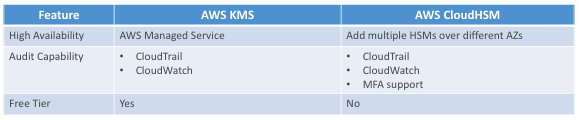
High Availability
- CloudHSM clusters are spread across Multi AZ (HA)
- Great for availability and durability
Integration with AWS Services
- Through integration with AWS KMS
- Configure KMS Custom Key Store with CloudHSM
- Example: EBS, S3, RDS …
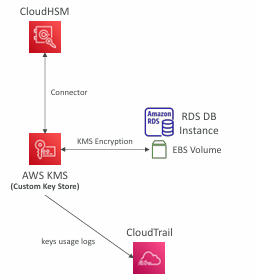
CloudHSM vs. KMS
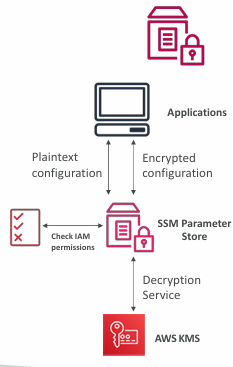
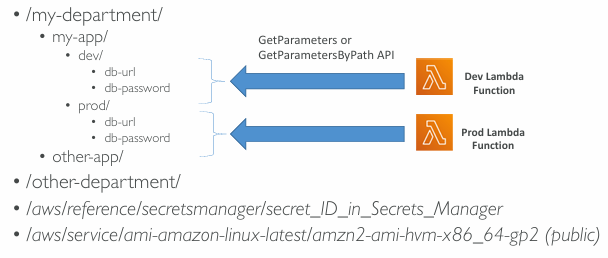
SSM Parameter Store
- Secure storage for configuration and secrets
- Optional Seamless Encryption using KMS
- Serverless, scalable, durable, easy SDK
- Version tracking of configurations / secrets
- Security through IAM
- Notifications with Amazon EventBridge
- Integration with CloudFormation
Hierarchy
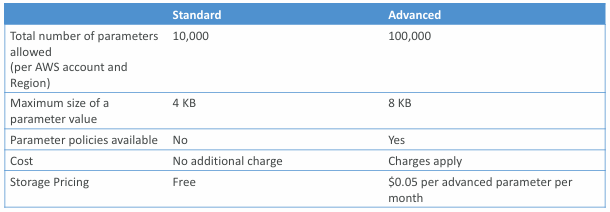
Standard and advanced parameter tiers
Parameters Policies (for advanced parameters)
- Allow to assign a TTL to a parameter (expiration date) to force updating or deleting sensitive data such as passwords
- Can assign multiple policies at a time

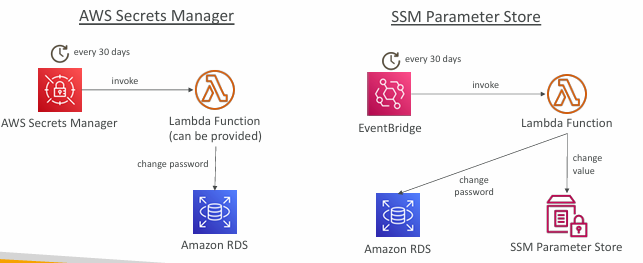
AWS Secrets Manager
- Newer service, meant for storing secrets
- Capability to force rotation of secrets every X days
- Automate generation of secrets on rotation (uses Lambda)
- Integration with Amazon RDS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Aurora)
- Secrets are encrypted using KMS
- Mostly meant for RDS integration
Multi-Region Secrets
- Replicate Secrets across multiple AWS Regions
- Secrets Manager keeps read replicas in sync with the primary Secret
- Ability to promote a read replica Secret to a standalone Secret
- Use cases: multi-region apps, disaster recovery strategies, multi-region DB…

SSM Parameter Store vs Secrets Manager
- Secrets Manager ($$$):
- Automatic rotation of secrets with AWS Lambda
- Lambda function is provided for RDS, Redshift, DocumentDB
- KMS encryption is mandatory
- Can integration with CloudFormation
- SSM Parameter Store ($):
- Simple API
- No secret rotation (can enable rotation using Lambda triggered by EventBridge)
- KMS encryption is optional
- Can integration with CloudFormation
- Can pull a Secrets Manager secret using the SSM Parameter Store API
Rotation
CloudFormation – Dynamic References

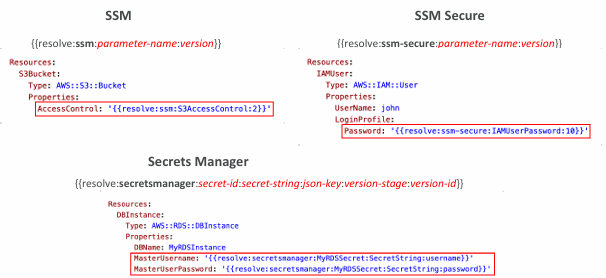
Option 1 – ManageMasterUserPassword
- ManageMasterUserPassword – creates admin secret implicitly
- RDS, Aurora will manage the secret in Secrets Manager and its rotation
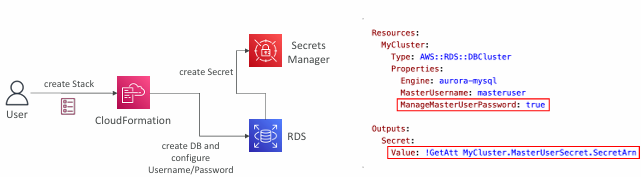
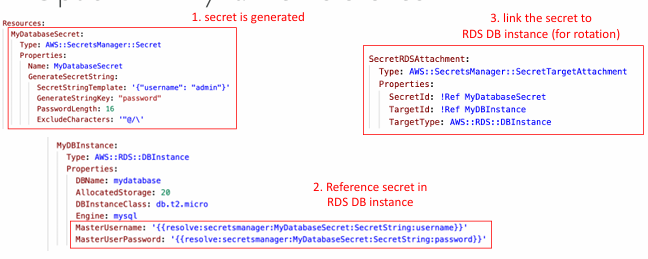
Option 2 – Dynamic Reference
CloudWatch Logs - Encryption
- You can encrypt CloudWatch logs with KMS keys
- Encryption is enabled at the log group level, by associating a CMK with a log group, either when you create the log group or after it exists.
- You cannot associate a CMK with a log group using the CloudWatch console.
- You must use the CloudWatch Logs API:
- associate-kms-key : if the log group already exists
- create-log-group: if the log group doesn’t exist yet
CodeBuild Security
- To access resources in your VPC, make sure you specify a VPC configuration for your CodeBuild
- Secrets in CodeBuild:
- Don’t store them as plaintext in environment variables
- Instead…
- Environment variables can reference parameter store parameters
- Environment variables can reference secrets manager secrets
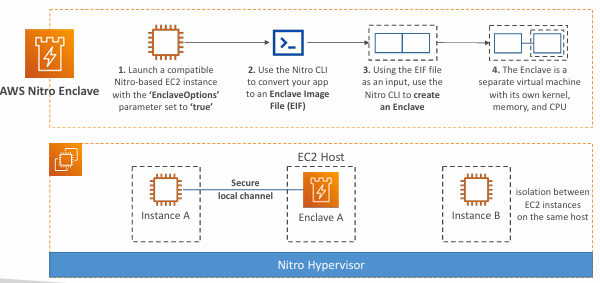
AWS Nitro Enclaves
- Process highly sensitive data in an isolated compute environment
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII), healthcare, financial, …
- Fully isolated virtual machines, hardened, and highly constrained
- Not a container, not persistent storage, no interactive access, no external networking
- Helps reduce the attack surface for sensitive data processing apps
- Cryptographic Attestation – only authorized code can be running in your Enclave
- Only Enclaves can access sensitive data (integration with KMS)
- Use cases: securing private keys, processing credit cards, secure multi-party computation…