Relational Databases (RDS/Aurora)
Relational Database Service (RDS)
- Managed DB service for DB use SQL as a query language
- It allows you to create databases in the cloud that are managed by AWS
- Postgres
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- IBM DB2
- Aurora (AWS Proprietary database)
Using RDS versus deploying DB on EC2
- RDS is a managed service:
- Automated provisioning, OS patching
- Continuous backups and restore to specific timestamp (Point in Time Restore)
- Monitoring dashboards
- Read replicas for improved read performance
- Multi AZ setup for DR (Disaster Recovery)
- Maintenance windows for upgrades
- Scaling capability (vertical and horizontal)
- Storage backed by EBS
- BUT you can’t SSH into your instances
Storage Auto Scaling
- Helps you increase storage on your RDS DB instance dynamically
- When RDS detects you are running out of free database storage, it scales automatically
- Avoid manually scaling your database storage
- You have to set Maximum Storage Threshold (maximum limit for DB storage)
- Automatically modify storage if:
- Free storage is less than 10% of allocated storage
- Low-storage lasts at least 5 minutes
- 6 hours have passed since last modification
- Useful for applications with unpredictable workloads
- Supports all RDS database engines
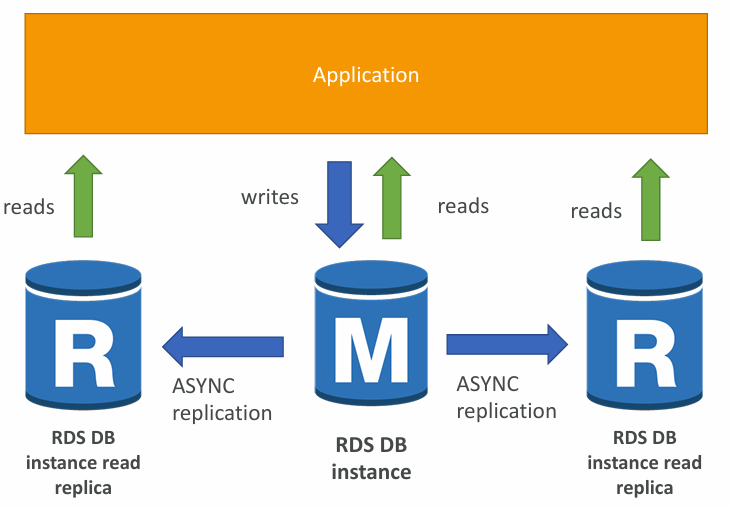
Read Replicas for read scalability
- Up to 15 Read Replicas
- Within AZ, Cross AZ or Cross Region
- Replication is ASYNC, so reads are eventually consistent
- Replicas can be promoted to their own DB
- Applications must update the connection string to leverage read replicas
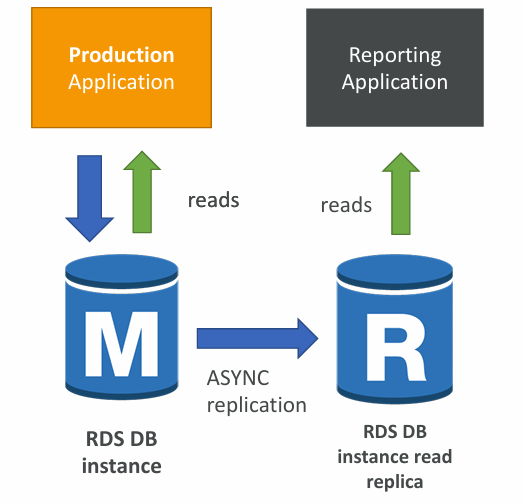
Example Use Case
- You have a production database that is taking on normal load
- You want to run a reporting application to run some analytics
- You create a Read Replica to run the new workload there
- The production application is unaffected
- Read replicas are only used for SELECT statements (not INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
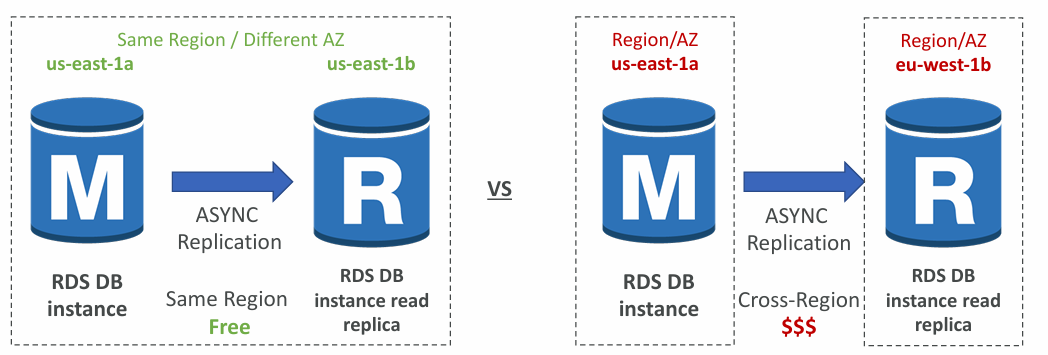
Read Replicas – Network Cost
- In AWS there’s a network cost when data goes from one AZ to another
- For RDS Read Replicas within the same region, you don’t pay that fee
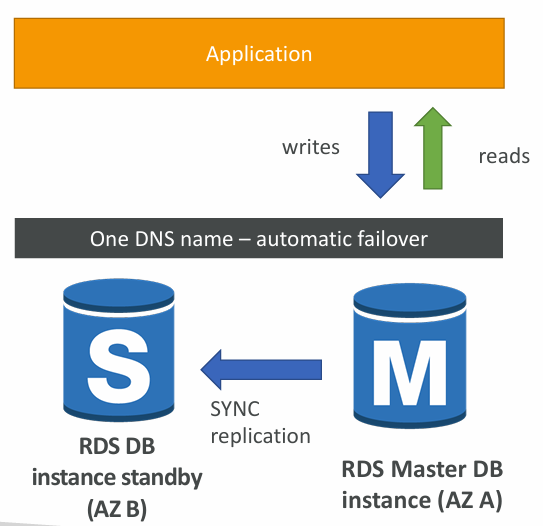
Multi AZ (Disaster Recovery)
- SYNC replication
- One DNS name – automatic app failover to standby
- Increases availability
- Failover in case of loss of AZ, loss of network, instance or storage failure
- No manual intervention in apps
- Not used for scaling
Note: The Read Replicas are setup as Multi AZ for Disaster Recovery (DR)
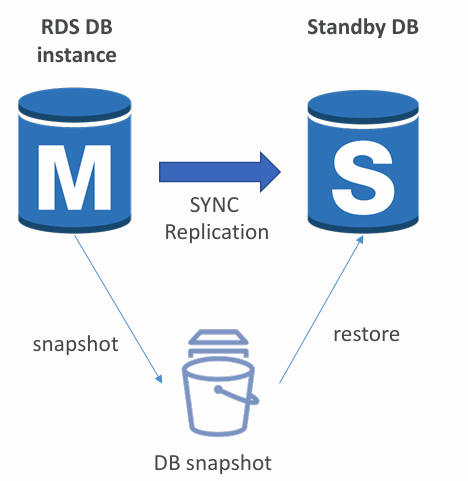
From Single-AZ to Multi-AZ
- Zero downtime operation (no need to stop the DB)
- Just click on “modify” for the database
- The following happens internally:
- A snapshot is taken
- A new DB is restored from the snapshot in a new AZ
- Synchronization is established between the two databases
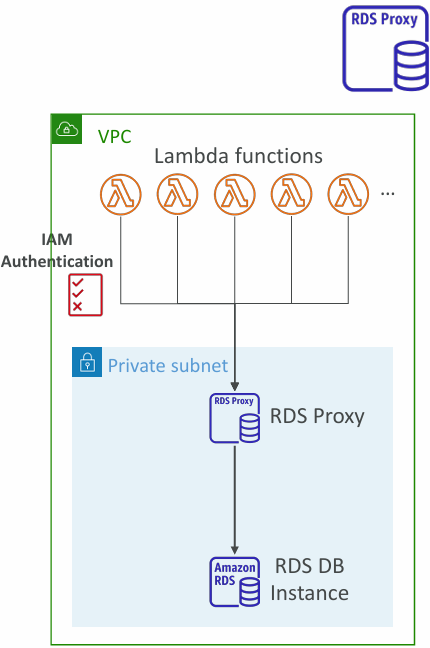
RDS Proxy
- Fully managed database proxy for RDS
- Allows apps to pool and share DB connections established with the database
- Improving database efficiency by reducing the stress on database resources (e.g., CPU, RAM) and minimize open connections (and timeouts)
- Serverless, autoscaling, highly available (multi-AZ)
- Reduced RDS & Aurora failover time by up 66%
- Supports RDS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, MS SQL Server) and Aurora (MySQL, PostgreSQL)
- No code changes required for most apps
- Enforce IAM Authentication for DB, and securely store credentials in AWS Secrets Manager
- RDS Proxy is never publicly accessible (must be accessed from VPC)
Amazon Aurora
- Aurora is a proprietary technology from AWS (not open sourced)
- Postgres and MySQL are both supported as Aurora DB (that means your drivers will work as if Aurora was a Postgres or MySQL database)
- Aurora is “AWS cloud optimized” and claims 5x performance improvement over MySQL on RDS, over 3x the performance of Postgres on RDS
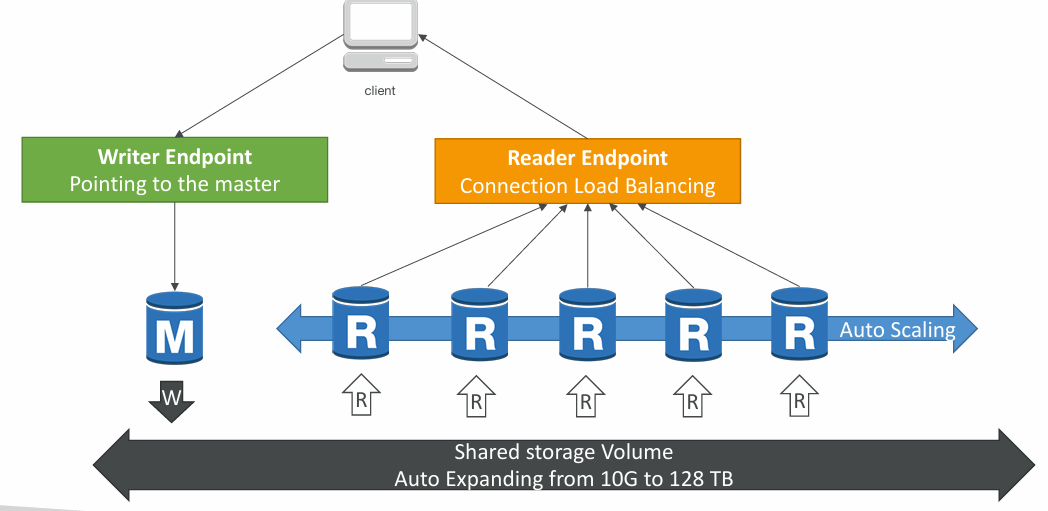
- Aurora storage automatically grows in increments of 10GB, up to 128 TB
- Aurora can have up to 15 replicas and the replication process is faster than MySQL (sub 10 ms replica lag)
- Failover in Aurora is instantaneous. It’s HA (High Availability) native
- Aurora costs more than RDS (20% more) – but is more efficient
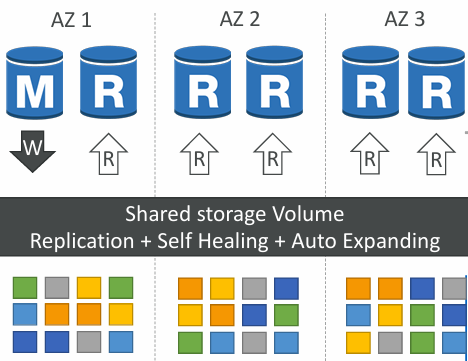
High Availability and Read Scaling
- 6 copies of your data across 3 AZ:
- 4 copies out of 6 needed for writes
- 3 copies out of 6 need for reads
- Self healing with peer-to-peer replication
- Storage is striped across 100s of volumes
- One Aurora Instance takes writes (master)
- Automated failover for master in less than 30 seconds
- Master + up to 15 Aurora Read Replicas serve reads
- Support for Cross Region Replication
DB Cluster
Features
- Automatic fail-over
- Backup and Recovery
- Isolation and security
- Industry compliance
- Push-button scaling
- Automated Patching with Zero Downtime
- Advanced Monitoring
- Routine Maintenance
- Backtrack: restore data at any point of time without using backups
RDS & Aurora Security
- At-rest encryption:
- Database master & replicas encryption using AWS KMS – must be defined as launch time
- If the master is not encrypted, the read replicas cannot be encrypted
- To encrypt an un-encrypted database, go through a DB snapshot & restore as encrypted
- In-flight encryption: TLS-ready by default, use the AWS TLS root certificates client-side
- IAM Authentication: IAM roles to connect to your database (instead of username/pw)
- Security Groups: Control Network access to your RDS / Aurora DB
- No SSH available except on RDS Custom
- Audit Logs can be enabled and sent to CloudWatch Logs for longer retention