- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Improves read performance, content is cached at the edge
- Improves users experience
- 216 Point of Presence globally (edge locations)
- DDoS protection (because worldwide), integration with Shield, AWS Web Application Firewall
Origins
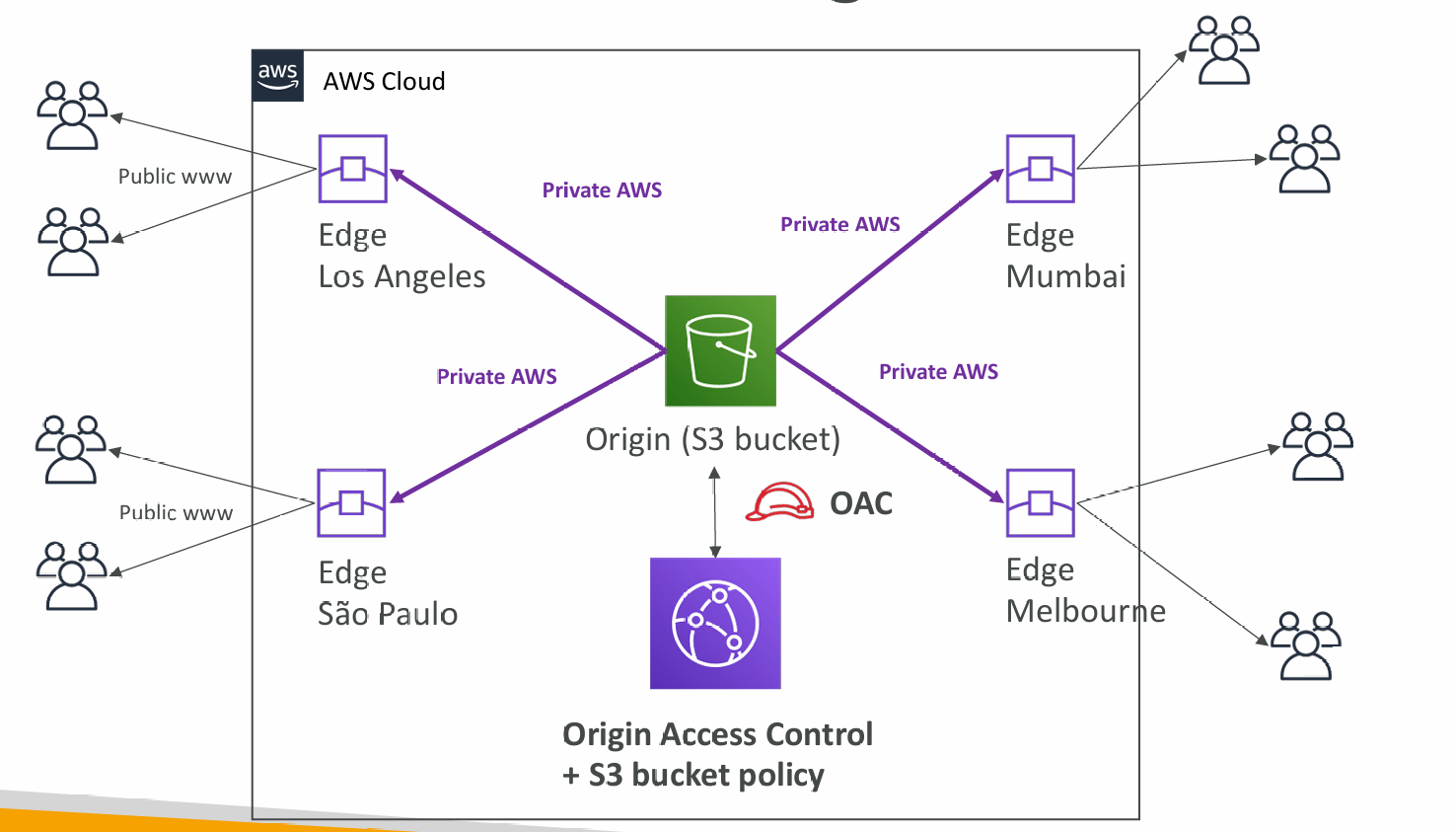
- S3 bucket
- For distributing files and caching them at the edge
- Enhanced security with CloudFront Origin Access Control (OAC)
- OAC is replacing Origin Access Identity (OAI)
- CloudFront can be used as an ingress (to upload files to S3)
- Custom Origin (HTTP)
- Application Load Balancer
- EC2 instance
- S3 website (must first enable the bucket as a static S3 website)
- Any HTTP backend you want
CloudFront vs S3 Cross Region Replication
- CloudFront:
- Global Edge network
- Files are cached for a TTL (maybe a day)
- Great for static content that must be available everywhere
- S3 Cross Region Replication:
- Must be setup for each region you want replication to happen
- Files are updated in near real-time
- Read only
- Great for dynamic content that needs to be available at low-latency in few regions
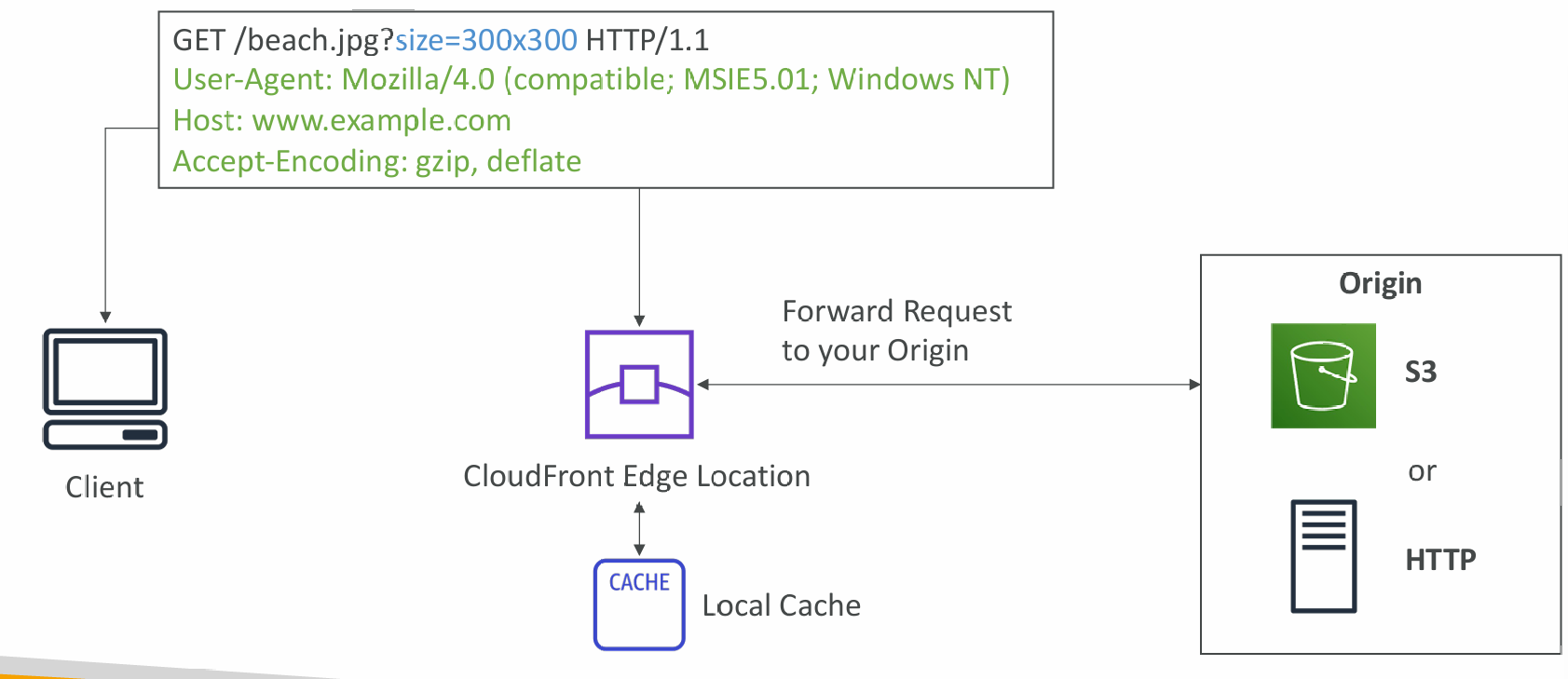
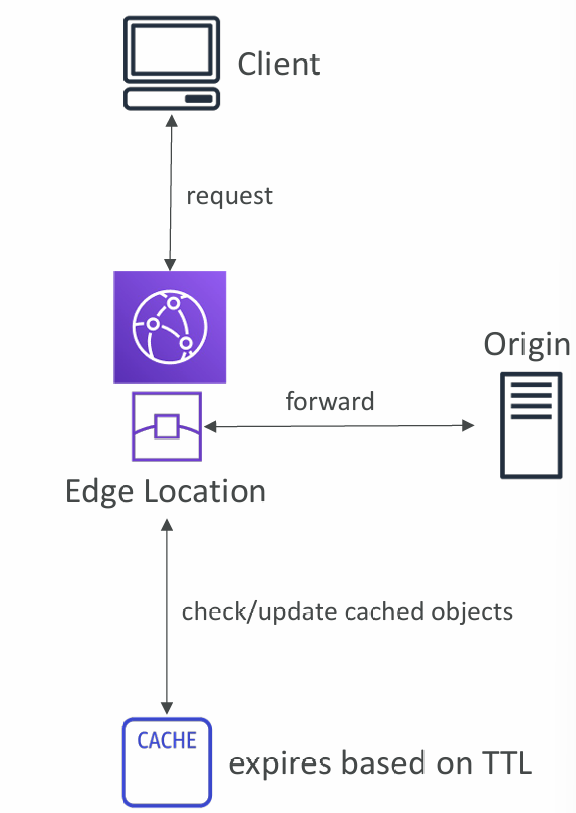
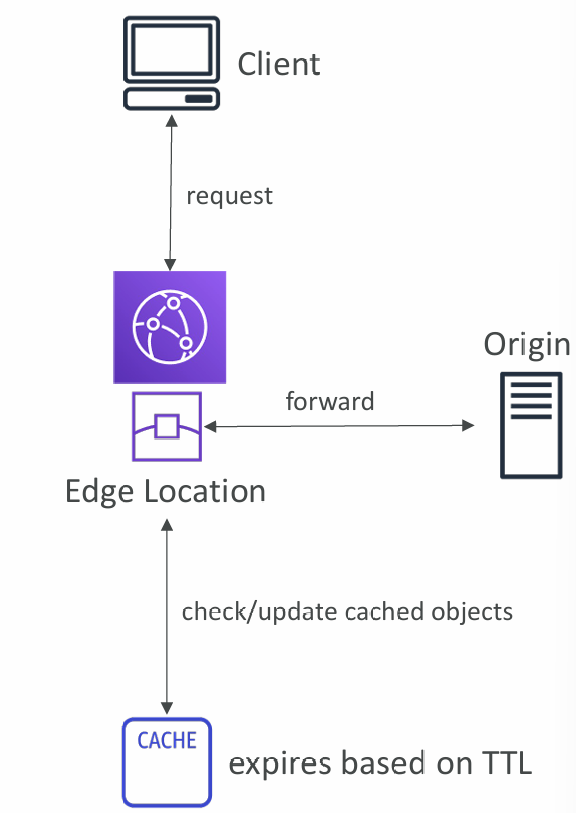
CloudFront Caching
- The cache lives at each CloudFront Edge Location
- CloudFront identifies each object in the cache using the Cache Key (see next slide)
- You want to maximize the Cache Hit ratio to minimize requests to the origin
- You can invalidate par t of the cache using the CreateInvalidation API
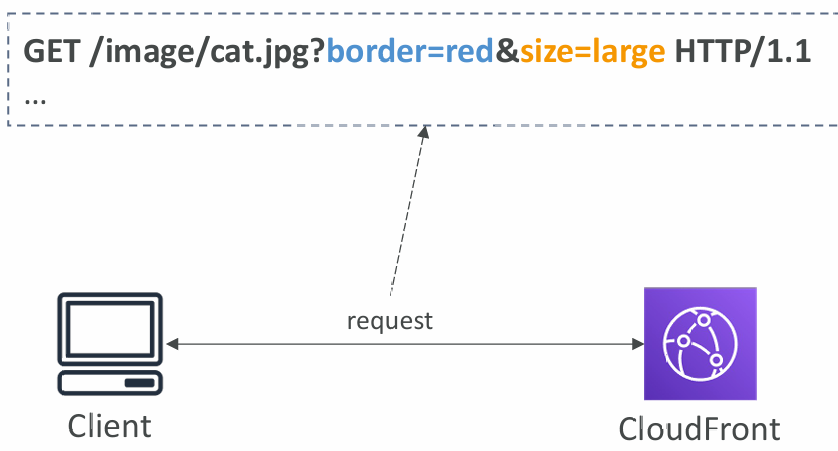
Cache Keys
- A unique identifier for every object in the cache
- By default, consists of hostname + resource portion of the URL
- If you have an application that serves up content that varies based on user, device, language, location…
- You can add other elements (HTTP headers, cookies, query strings) to the Cache Key using CloudFront Cache Policies
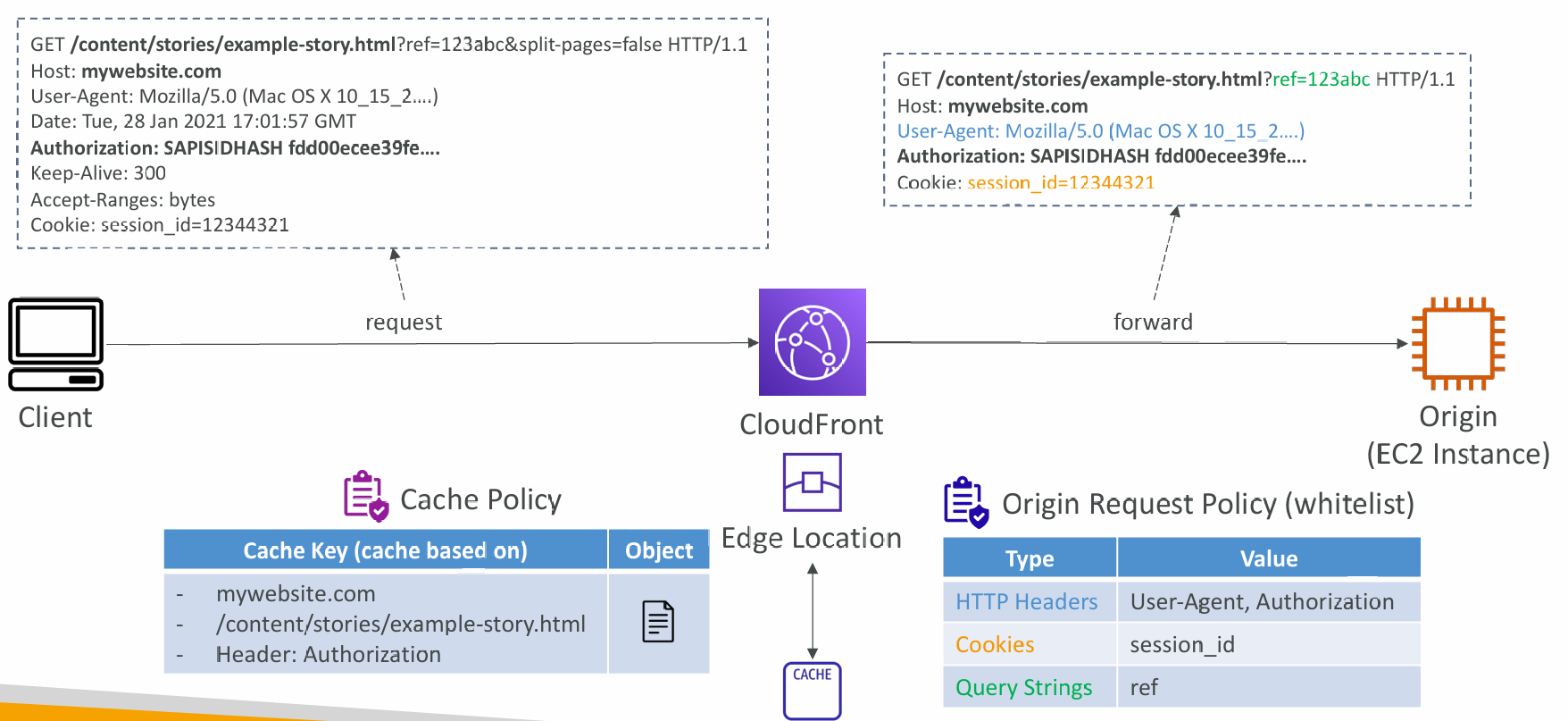
Cache Policy
- Cache based on:
- HTTP Headers: None – Whitelist
- Cookies: None – Whitelist – Include All-Except – All
- Query Strings: None – Whitelist – Include All-Except – All
- Control the TTL (0 seconds to 1 year), can be set by the origin using the Cache-Control header, Expires header…
- Create your own policy or use Predefined Managed Policies
- All HTTP headers, cookies, and query strings that you include in the Cache Key are automatically included in origin requests
- None:
- Don’t include any headers in the Cache Key (except default)
- Headers are not forwarded (except default)
- Best caching performance
- Whitelist:
- only specified headers included in the Cache Key
- Specified headers are also forwarded to Origin
Cache Policy Query Strings
- None
- Don’t include any query strings in the Cache Key
- Query strings are not forwarded
- Whitelist
- Only specified query strings included in the Cache Key
- Only specified query strings are forwarded
- Include All-Except
- Include all query strings in the Cache Key except the specified list
- All query strings are forwarded except the specified list
- All
- Include all query strings in the Cache Key
- All query strings are forwarded
- Worst caching performance
Origin Request Policy
- Specify values that you want to include in origin requests without including them in the Cache Key (no duplicated cached content)
- You can include:
- HTTP headers: None – Whitelist – All viewer headers options
- Cookies: None – Whitelist – All
- Query Strings: None – Whitelist – All
- Ability to add CloudFront HTTP headers and Custom Headers to an origin request that were not included in the viewer request
- Create your own policy or use Predefined Managed Policies
Cache Policy vs. Origin Request Policy
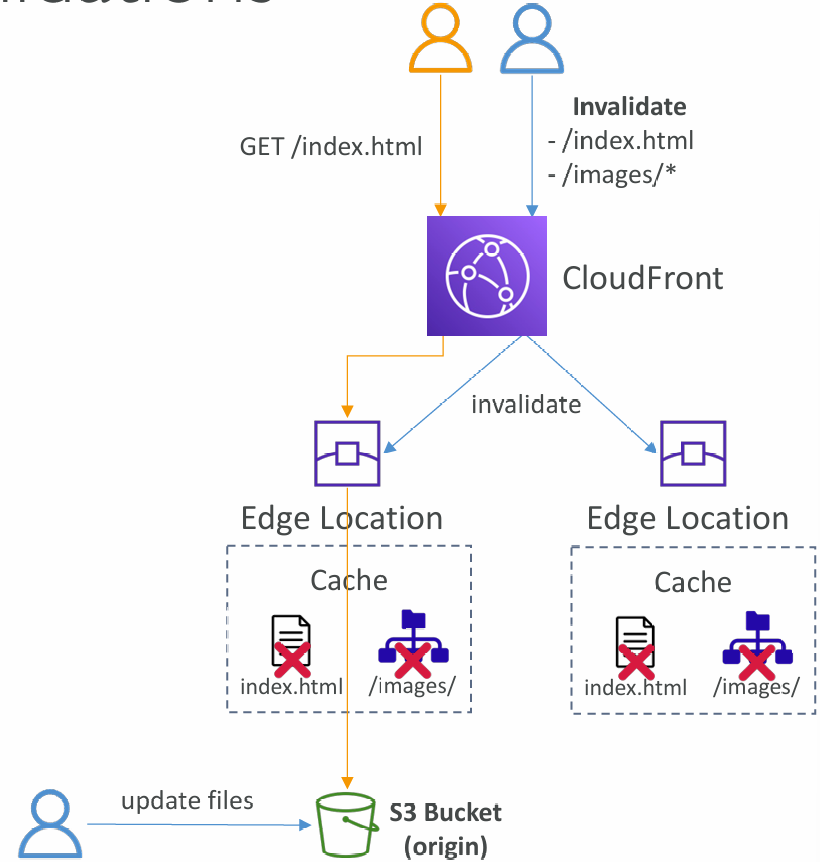
Cache Invalidations
- In case you update the back-end origin, CloudFront doesn’t know about it and will only get the refreshed content after the TTL has expired
- However, you can force an entire or partial cache refresh (thus bypassing the TTL) by performing a CloudFront Invalidation
- You can invalidate all files (*) or a special path (/images/*)
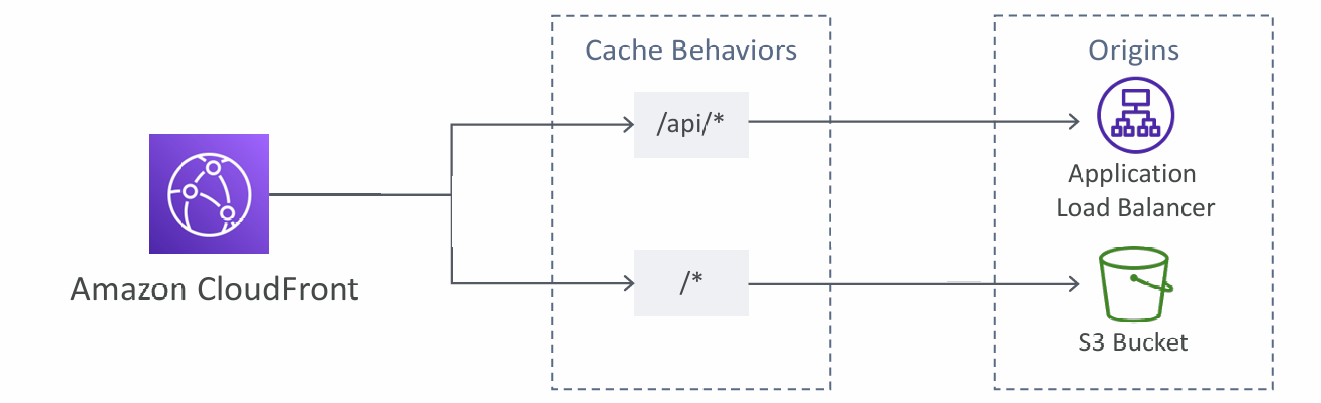
Cache Behaviors
- Configure different settings for a given URL path pattern
- Example: one specific cache behavior to images/*.jpg files on your origin web server
- Route to different kind of origins/origin groups based on the content type or path pattern
- /images/*
- /api/*
- /* (default cache behavior)
- When adding additional Cache Behaviors, the Default Cache Behavior is always the last to be processed and is always /*
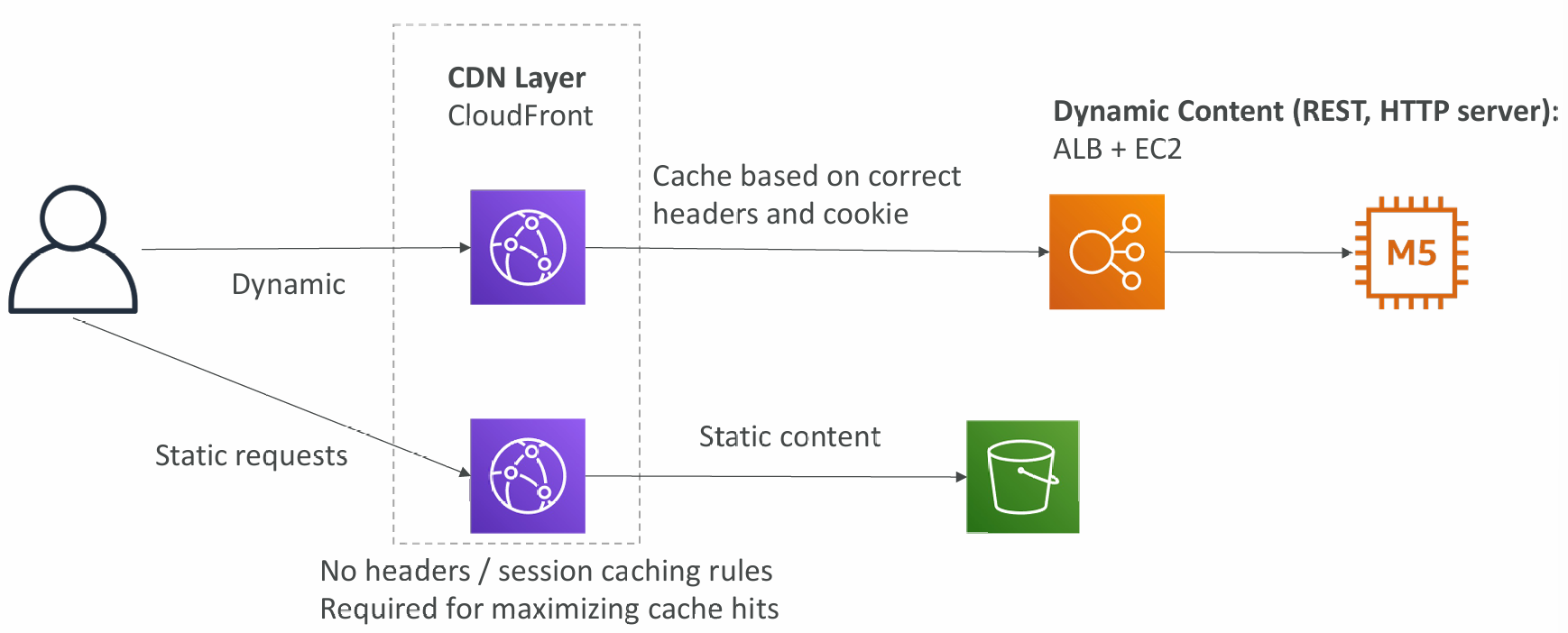
Sign In Page
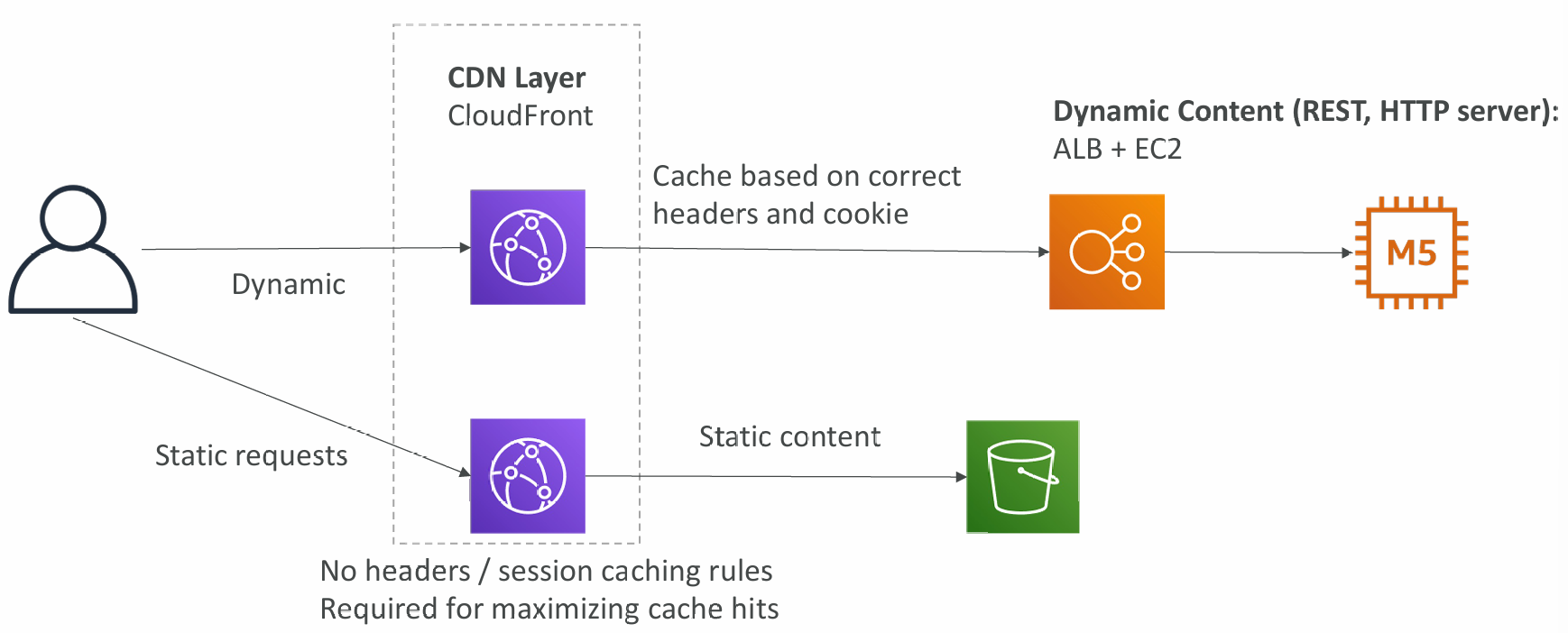
Maximize cache hits by separating static and dynamic distributions
ALB or EC2 as an origin
CloudFront Geo Restriction
- You can restrict who can access your distribution:
- Allowlist: Allow your users to access your content only if they're in one of the countries on a list of approved countries.
- Blocklist: Prevent your users from accessing your content if they're in one of the countries on a list of banned countries
- The “country” is determined using a 3rd party Geo-IP database
- Use case: Copyright Laws to control access to content
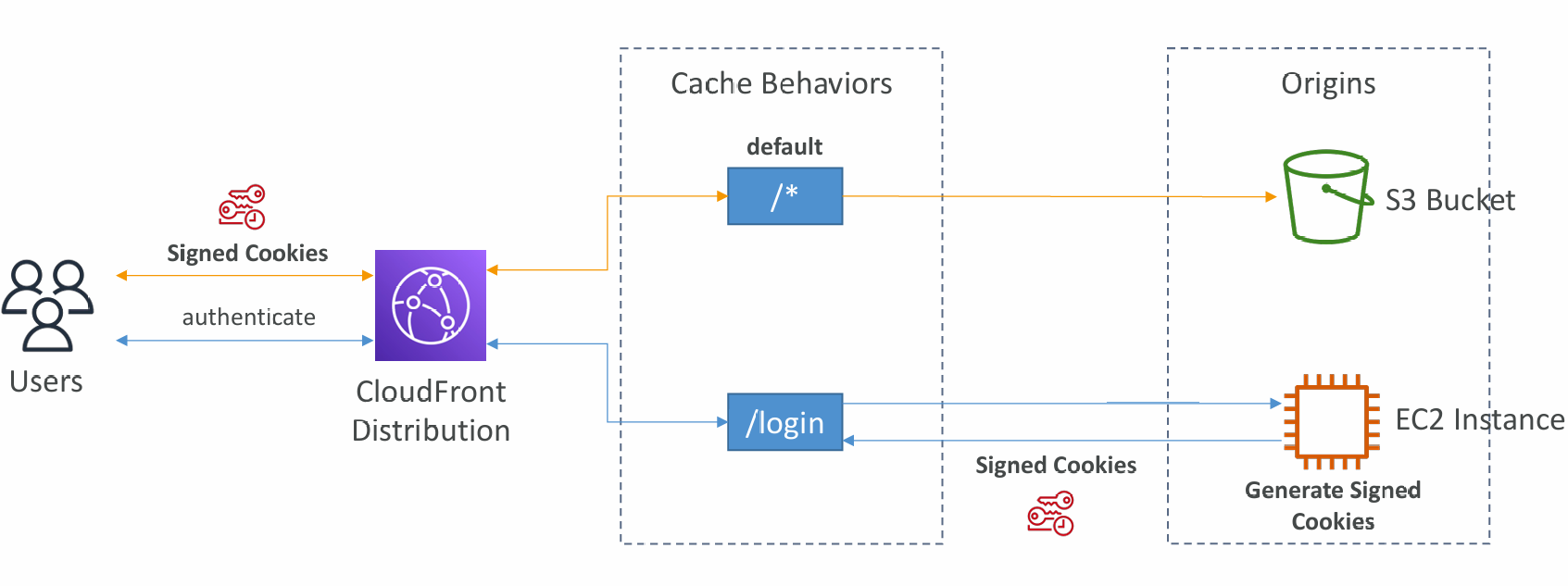
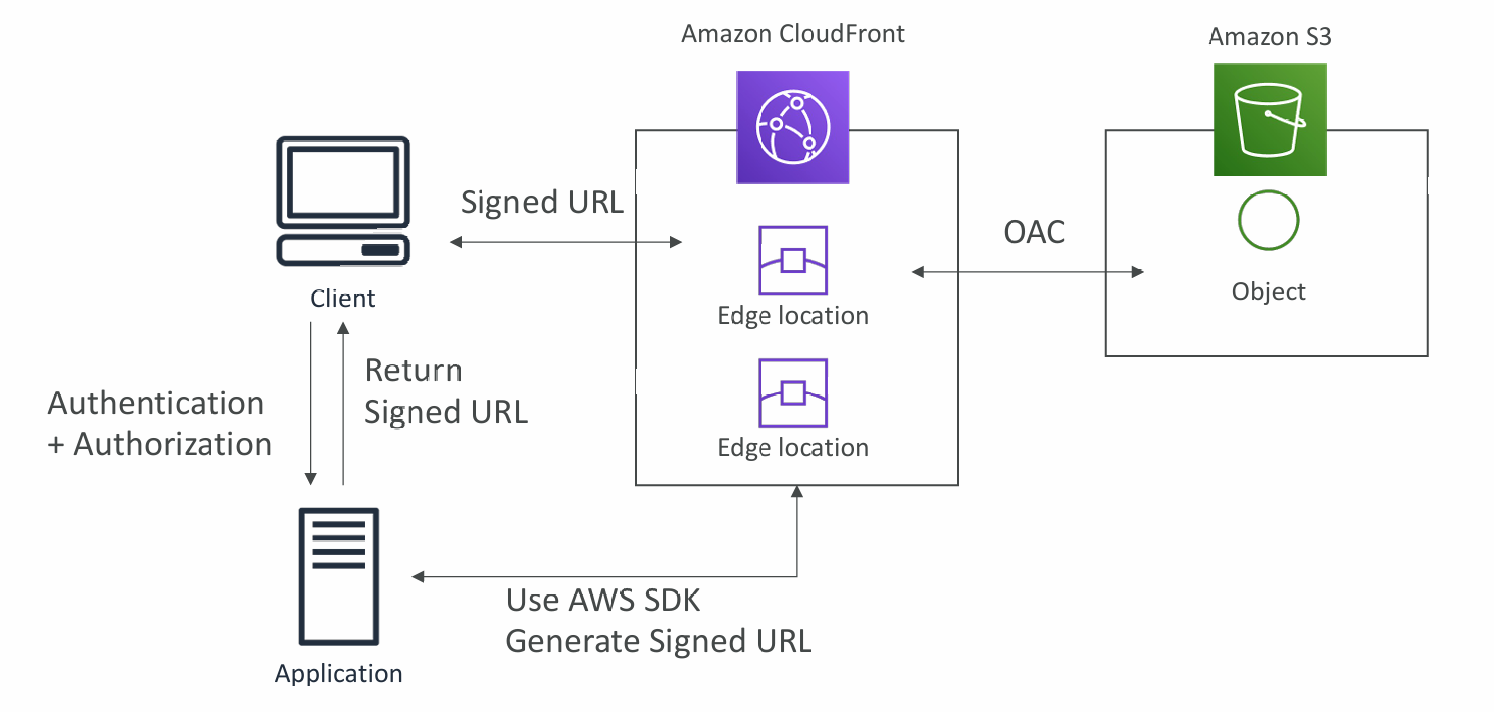
Signed URL / Signed Cookies
- You want to distribute paid shared content to premium users over the world
- We can use CloudFront Signed URL / Cookie. We attach a policy with:
- Includes URL expiration
- Includes IP ranges to access the data from
- Trusted signers (which AWS accounts can create signed URLs)
- How long should the URL be valid for?
- Shared content (movie, music): make it short (a few minutes)
- Private content (private to the user): you can make it last for years
- Signed URL = access to individual files (one signed URL per file)
- Signed Cookies = access to multiple files (one signed cookie for many files)
CloudFront Signed URL Diagram
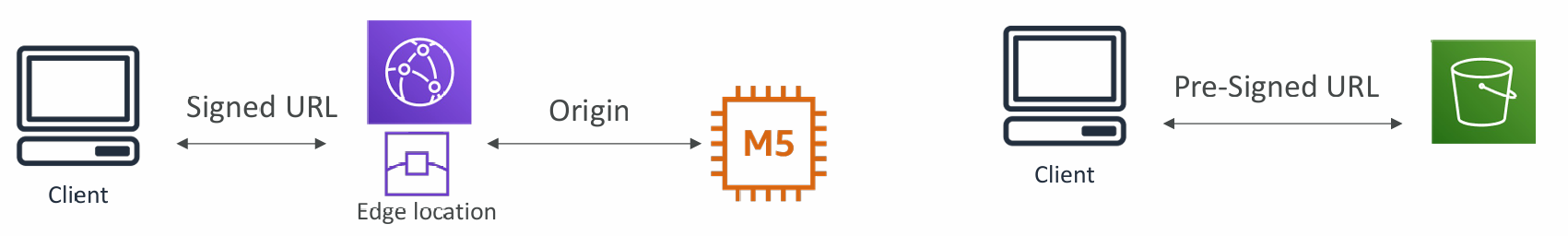
Signed URL vs S3 Pre-Signed URL
- CloudFront Signed URL:
- Allow access to a path, no matter the origin
- Account wide key-pair, only the root can manage it
- Can filter by IP, path, date, expiration
- Can leverage caching features
- S3 Pre-Signed URL:
- Issue a request as the person who pre-signed the URL
- Uses the IAM key of the signing IAM principal
- Limited lifetime
Signed URL Process
- Two types of signers:
- Either a trusted key group (recommended)
- Can leverage APIs to create and rotate keys (and IAM for API security)
- An AWS Account that contains a CloudFront Key Pair
- Need to manage keys using the root account and the AWS console
- Not recommended because you shouldn’t use the root account for this
- In your CloudFront distribution, create one or more trusted key groups
- You generate your own public / private key
- The private key is used by your applications (e.g. EC2) to sign URLs
- The public key (uploaded) is used by CloudFront to verify URLs
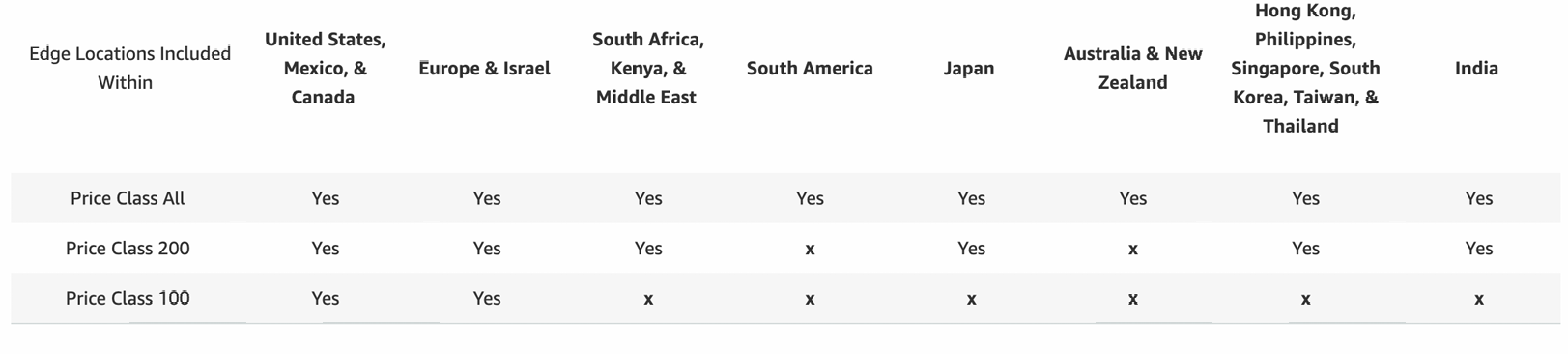
Pricing
- CloudFront Edge locations are all around the world
- The cost of data out per edge location varies
- You can reduce the number of edge locations for cost reduction
- Three price classes:
- Price Class All: all regions – best performance
- Price Class 200: most regions, but excludes the most expensive regions
- Price Class 100: only the least expensive regions
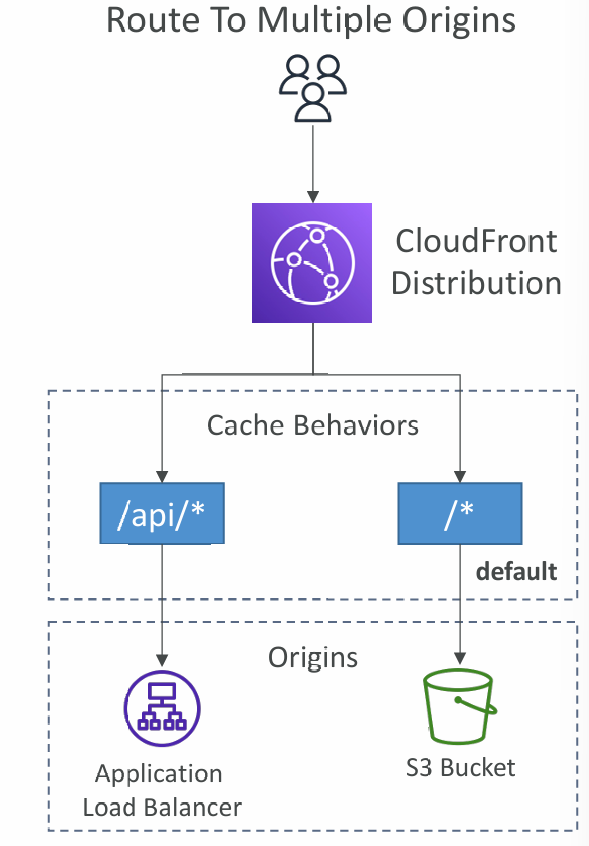
Multiple Origin
- To route to different kind of origins based on the content type
- Based on path pattern:
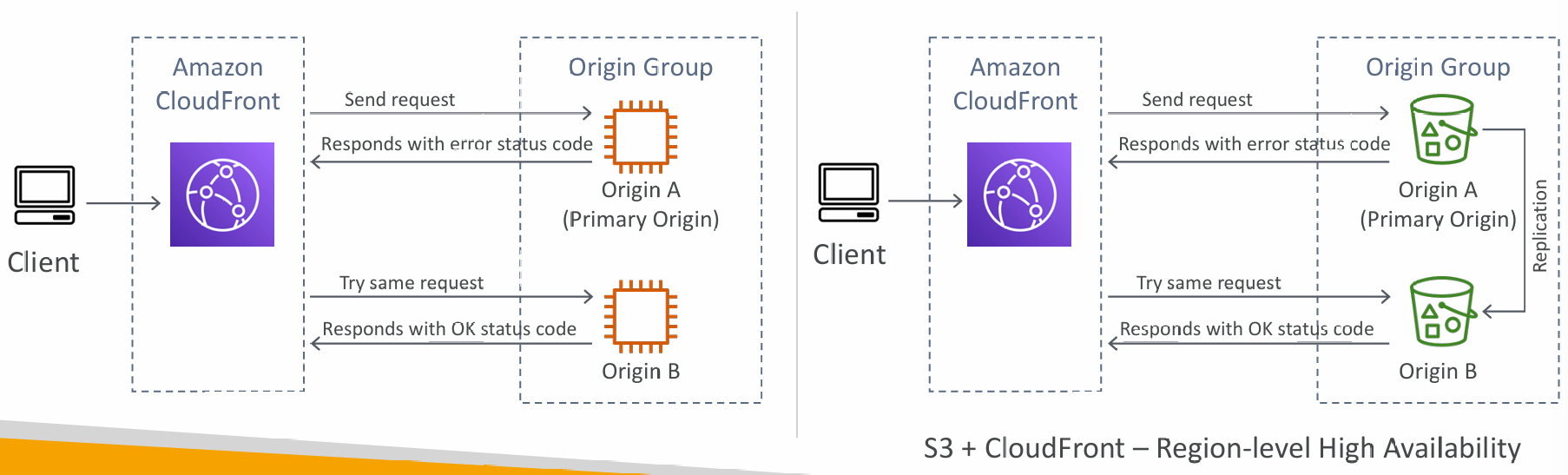
Origin Groups
- To increase high-availability and do failover
- Origin Group: one primary and one secondary origin
- If the primary origin fails, the second one is used
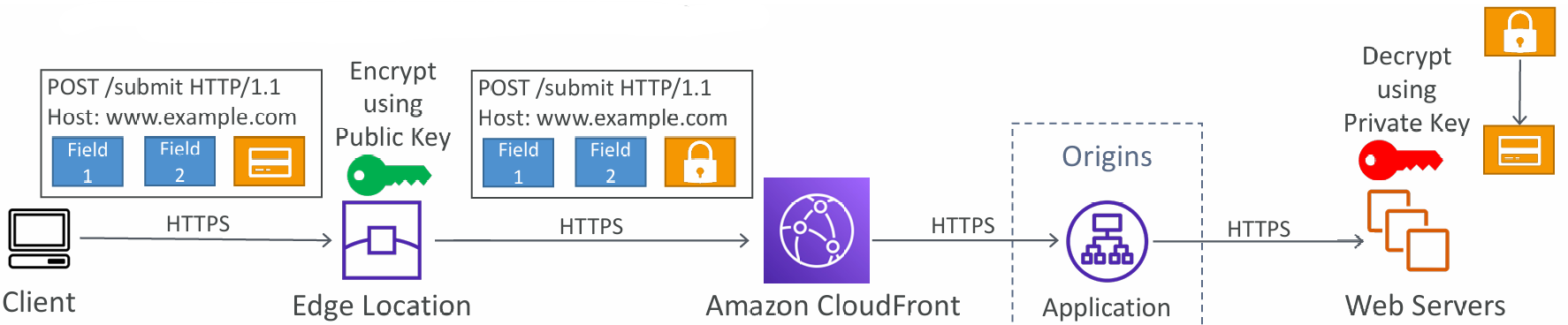
Field Level Encryption
- Protect user sensitive information through application stack
- Adds an additional layer of security along with HTTPS
- Sensitive information encrypted at the edge close to user
- Uses asymmetric encryption
- Usage:
- Specify set of fields in POST requests that you want to be encrypted (up to 10 fields)
- Specify the public key to encrypt them
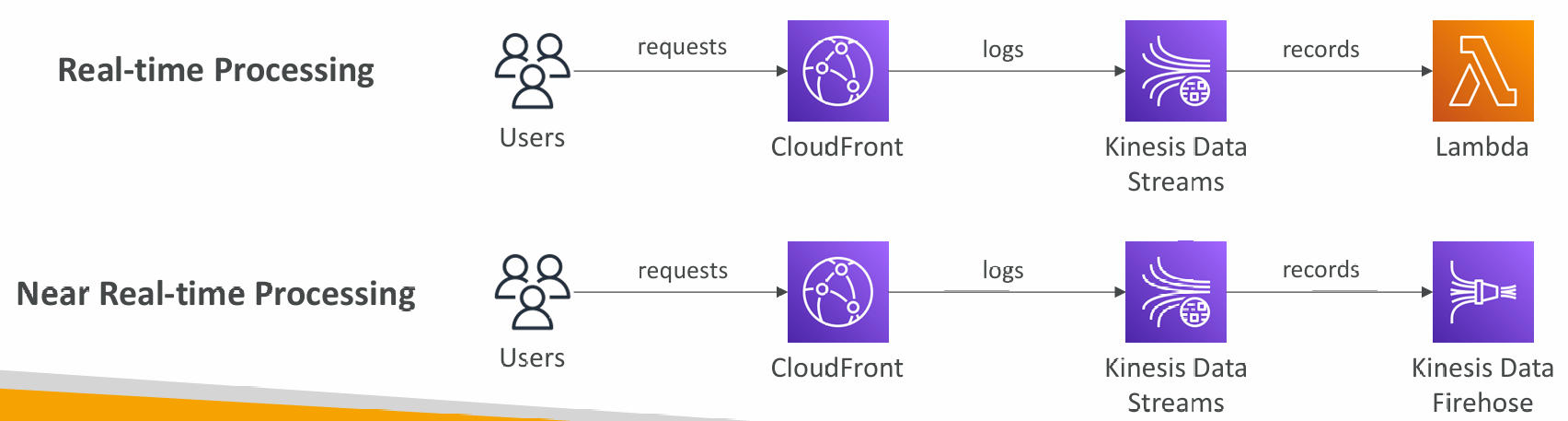
Real Time Logs
- Get real-time requests received by CloudFront sent to Kinesis Data Streams
- Monitor, analyze, and take actions based on content delivery performance
- Allows you to choose:
- Sampling Rate – percentage of requests for which you want to receive
- Specific fields and specific Cache Behaviors (path patterns)