Cloud AWS Certified Developer Associate Miscellaneous Serverless On this page
AWS Step Functions
Model your workflows as state machines (one per workflow)
Order fulfillment, Data processing
Web applications, Any workflow
Written in JSON
Visualization of the workflow and the execution of the workflow, as well as history
Start workflow with SDK call, API Gateway, Event Bridge (CloudWatch Event)
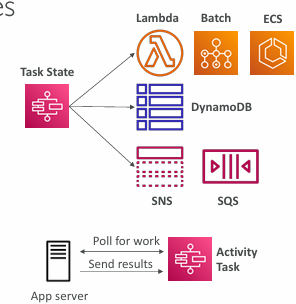
Task States
Do some work in your state machine
Invoke one AWS service
Can invoke a Lambda function
Run an AWS Batch job
Run an ECS task and wait for it to complete
Insert an item from DynamoDB
Publish message to SNS, SQS
Launch another Step Function workflow…
Run an one Activity
EC2, Amazon ECS, on-premises
Activities poll the Step functions for work
Activities send results back to Step Functions
States
Choice State - Test for a condition to send to a branch (or default branch)Fail or Succeed State - Stop execution with failure or successPass State - Simply pass its input to its output or inject some fixed data, without performing work.Wait State - Provide a delay for a certain amount of time or until a specified time/date.Map State - Dynamically iterate steps.’Parallel State - Begin parallel branches of execution.
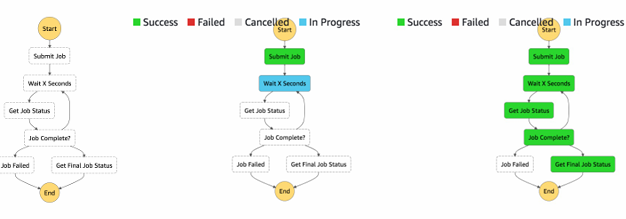
Visual workflow
Error Handling
Any state can encounter runtime errors for various reasons:
State machine definition issues (for example, no matching rule in a Choice state)
Task failures (for example, an exception in a Lambda function)
Transient issues (for example, network partition events)
Use Retry (to retry failed state) and Catch (transition to failure path) in the State Machine to handle the errors instead of inside the Application Code
Predefined error codes:
States.ALL : matches any error name
States.Timeout: Task ran longer than TimeoutSeconds or no heartbeat received
States.TaskFailed: execution failure
States.Permissions: insufficient privileges to execute code
The state may report is own errors
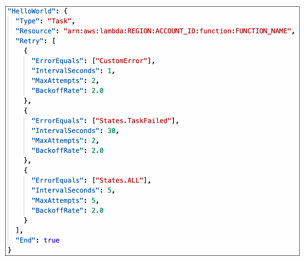
Retry (Task or Parallel State)
Evaluated from top to bottom
ErrorEquals : match a specific kind of errorIntervalSeconds : initial delay before retryingBackoffRate : multiple the delay after each retryMaxAttempts : default to 3, set to 0 for never retriedWhen max attempts are reached, the Catch kicks in
Catch (Task or Parallel State)
Evaluated from top to bottom
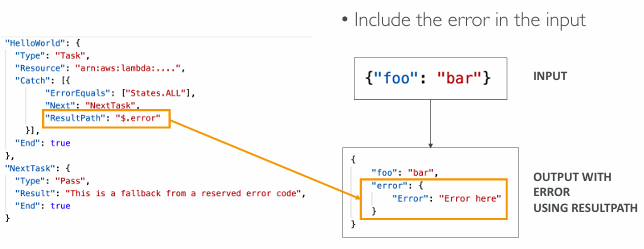
ErrorEquals : match a specific kind of errorNext : State to send toResultPath : A path that determines what input is sent to the state specified in the Next field
ResultPath
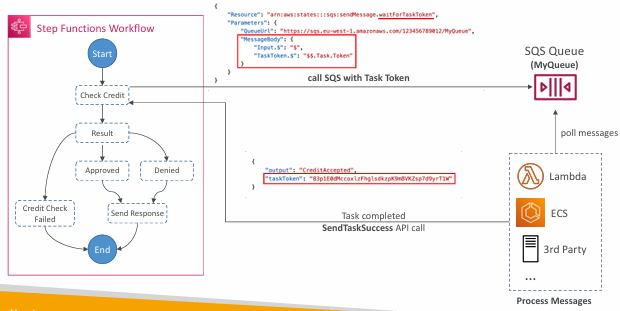
Wait for Task Token
Allows you to pause Step Functions during a Task until a Task Token is returned
Task might wait for other AWS ser vices, human approval, 3rd party integration, call legacy systems…
Append .waitForTaskToken to the Resource field to tell Step Functions to wait for the Task Token to be returned
Task will pause until it receives that Task Token back with a SendTaskSuccess or SendTaskFailure API call
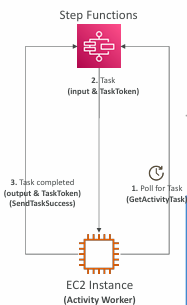
Activity Tasks
Enables you to have the Task work performed by an Activity Worker
Activity Worker apps can be running on EC2, Lambda, mobile device…
Activity Worker poll for a Task using GetActivityTask API
After Activity Worker completes its work, it sends a response of its success/failure using SendTaskSuccess or SendTaskFailure
To keep the Task active:
Configure how long a task can wait by setting TimeoutSeconds
Periodically send a heartbeat from your Activity Worker using SendTaskHeartBeat within the time you set in HeartBeatSeconds
By configuring a long TimeoutSeconds and actively sending a heartbeat, Activity Task can wait up to 1 year
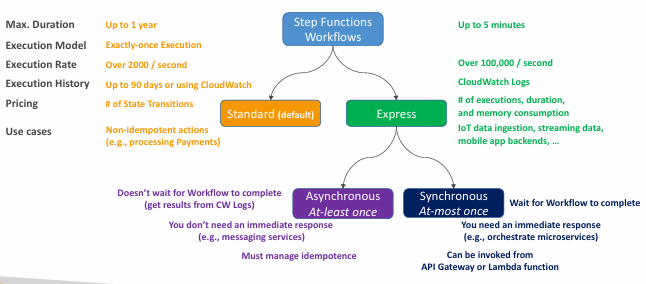
Standard vs. Express
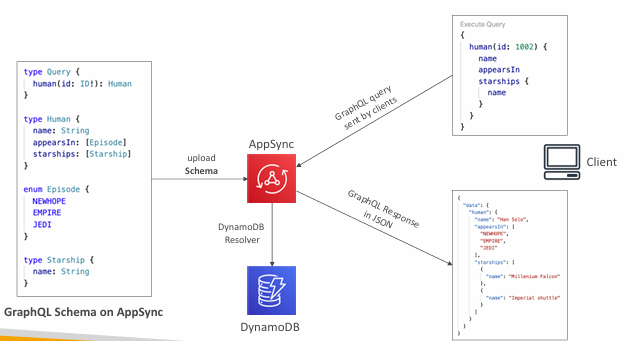
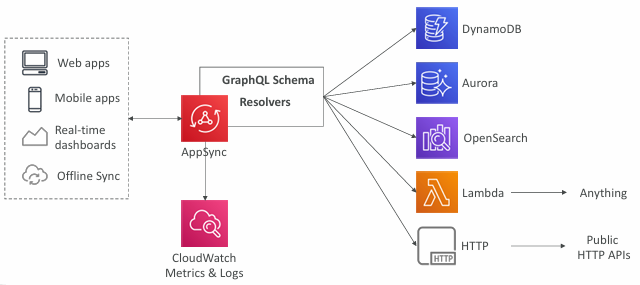
AWS AppSync
AppSync is a managed service that uses GraphQL
GraphQL makes it easy for applications to get exactly the data they need.
This includes combining data from one or more sources
NoSQL data stores, Relational databases, HTTP APIs…
Integrates with DynamoDB, Aurora, OpenSearch & others
Custom sources with AWS Lambda
Retrieve data in real-time with WebSocket or MQTT on WebSocket
For mobile apps: local data access & data synchronization
It all starts with uploading one GraphQL schema
GraphQL Example
AppSync Diagram
Security
There are four ways you can authorize applications to interact with your AWS AppSync GraphQL API:
API_KEY
AWS_IAM: IAM users / roles / cross-account access
OPENID_CONNECT: OpenID Connect provider / JSON Web Token
AMAZON_COGNITO_USER_POOLS
For custom domain & HTTPS, use CloudFront in front of AppSync
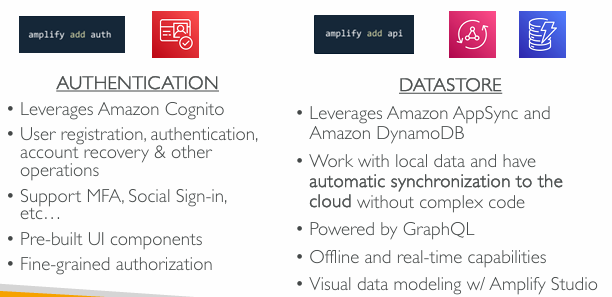
AWS Amplify
Set of tools to get started with creating mobile and web applications
“Elastic Beanstalk for mobile and web applications”
Must-have features such as data storage, authentication, storage, and machine-learning, all powered by AWS services
Front-end libraries with ready-to-use components for React.js, Vue, Javascript, iOS, Android, Flutter, etc…
Incorporates AWS best practices to for reliability, security, scalability
Amplify Studio: Visually build full-stack app, FE and BEAmplify CLI: Configure an Amplify backend with a guided CLI workflowAmplify Libraries: Connect your app to existing AWS services (Cognito, S3 and more)Amplify Hosting: Host apps or websites via the AWS content deliver network
Important Features
Amplify Hosting
Build and Host Modern Web Apps
CICD (build, test, deploy)
Pull Request Previews
Custom Domains
Monitoring
Redirect and Custom Headers
Password protection
End-to-End (E2E) Testing