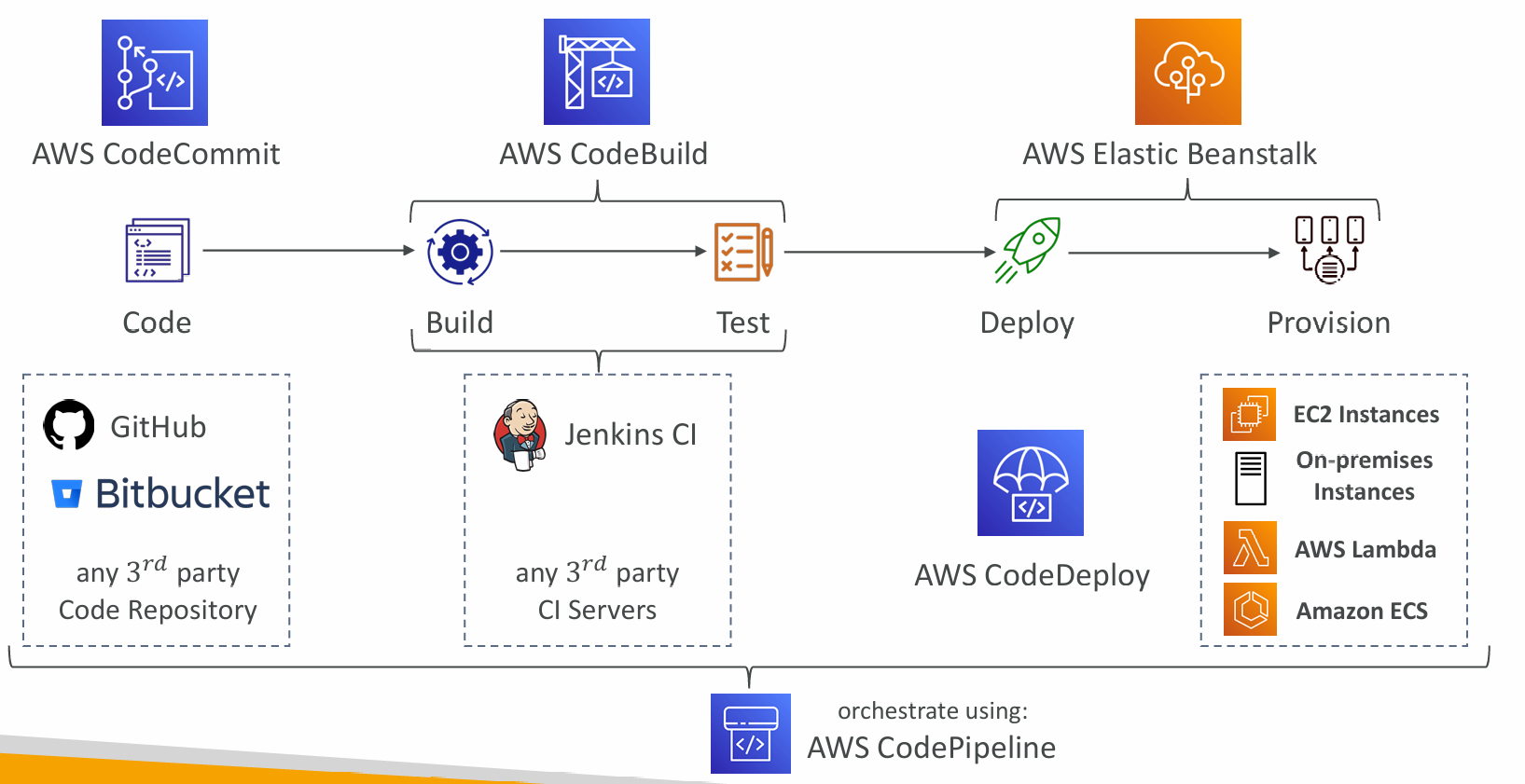
- AWS CodeCommit – storing our code
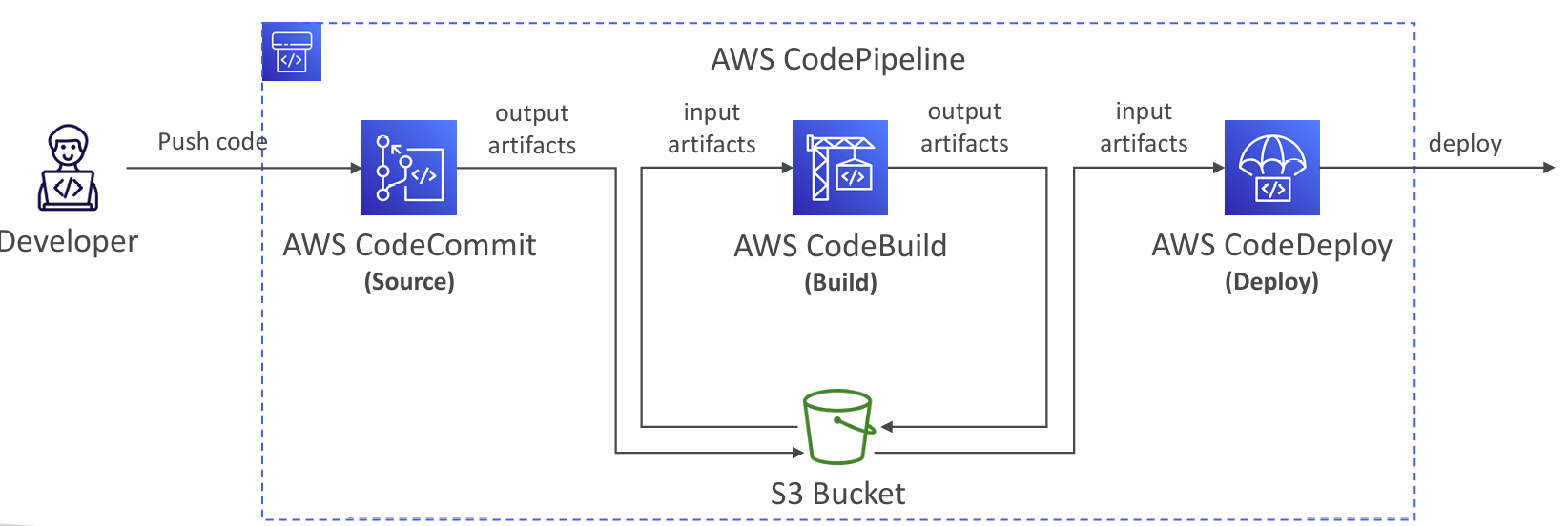
- AWS CodePipeline – automating our pipeline from code to Elastic Beanstalk
- AWS CodeBuild – building and testing our code
- AWS CodeDeploy – deploying the code to EC2 instances (not Elastic Beanstalk)
- AWS CodeStar – manage software development activities in one place
- AWS CodeArtifact – store, publish, and share software packages
- AWS CodeGuru – automated code reviews using Machine Learning
CodeCommit (discontinued)
- Private Git repositories
- No size limit on repositories (scale seamlessly)
- Fully managed, highly available
- Code only in AWS Cloud account => increased security and compliance
- Security (encrypted, access control, …)
- Integrated with Jenkins, AWS CodeBuild, and other CI tools
Security
- Interactions are done using Git (standard)
- Authentication
- SSH Keys – AWS Users can configure SSH keys in their IAM Console
- HTTPS – with AWS CLI Credential helper or Git Credentials for IAM user
- Authorization
- IAM policies to manage users/roles permissions to repositories
- Encryption
- Repositories are automatically encrypted at rest using AWS KMS
- Encrypted in transit (can only use HTTPS or SSH – both secure)
- Cross-account Access
- Do NOT share your SSH keys or your AWS credentials
- Use an IAM Role in your AWS account and use AWS STS (AssumeRole API)
CodePipeline
- Visual Workflow to orchestrate your CICD
- Source – CodeCommit, ECR, S3, Bitbucket, GitHub
- Build – CodeBuild, Jenkins, CloudBees, TeamCity
- Test – CodeBuild, AWS Device Farm, 3rd party tools, …
- Deploy – CodeDeploy, Elastic Beanstalk, CloudFormation, ECS, S3, …
- Invoke – Lambda, Step Functions
- Consists of stages:
- Each stage can have sequential actions and/or parallel actions
- Example: Build è Test è Deploy è Load Testing è …
- Manual approval can be defined at any stage
- Each pipeline stage can create artifacts
- Artifacts stored in an S3 bucket and passed on to the next stage
Troubleshooting
- For CodePipeline Pipeline/Action/Stage Execution State Changes
- Use CloudWatch Events (Amazon EventBridge). Example:
- You can create events for failed pipelines
- You can create events for cancelled stages
- If CodePipeline fails a stage, your pipeline stops, and you can get information in the console
- If pipeline can’t perform an action, make sure the “IAM Service Role” attached does have enough IAM permissions (IAM Policy)
- AWS CloudTrail can be used to audit AWS API calls
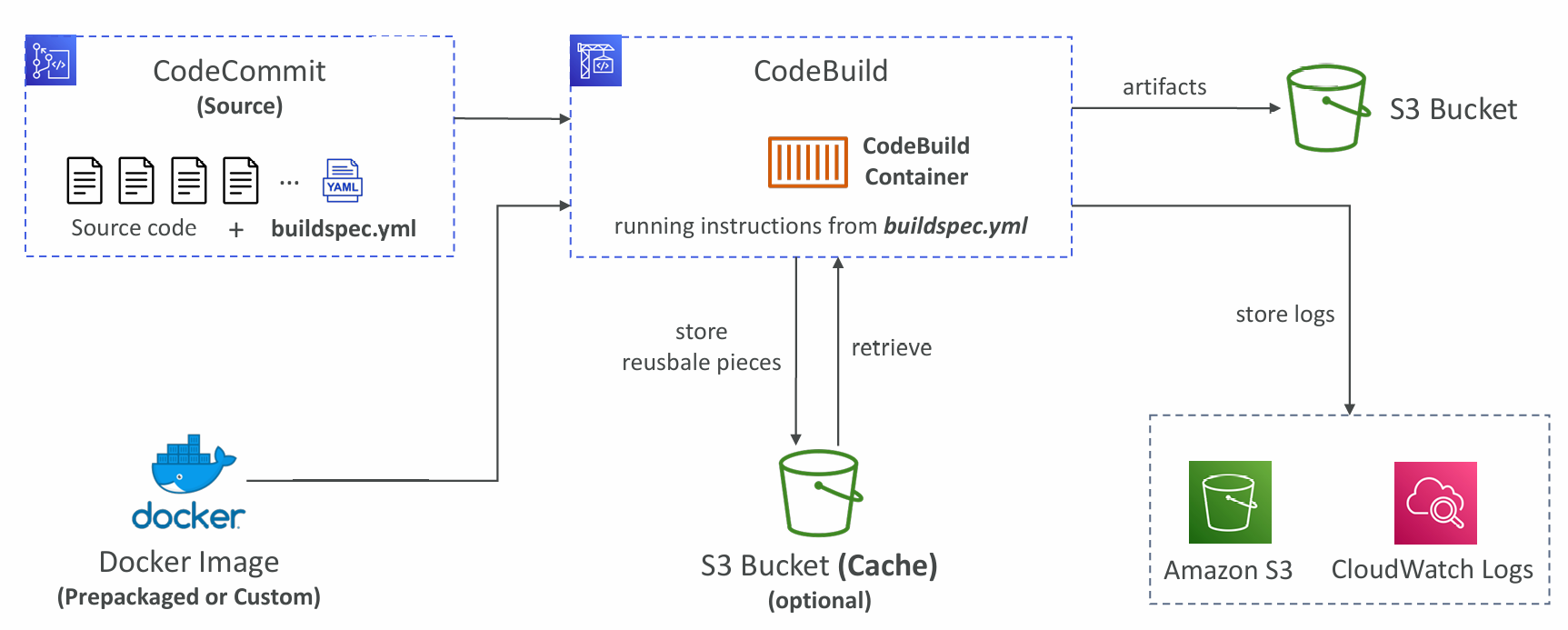
CodeBuild
- A fully managed continuous integration (CI) service
- Continuous scaling (no servers to manage or provision – no build queue)
- Compile source code, run tests, produce software packages, …
- Alternative to other build tools (e.g., Jenkins)
- Charged per minute for compute resources (time it takes to complete the builds)
- Leverages Docker under the hood for reproducible builds
- Use prepackaged Docker images or create your own custom Docker image
- Security:
- Integration with KMS for encryption of build artifacts
- IAM for CodeBuild permissions, and VPC for network security
- AWS CloudTrail for API calls logging
- Source – CodeCommit, S3, Bitbucket, GitHub
- Build instructions: Code file buildspec.yml or insert manually in Console
- Output logs can be stored in Amazon S3 & CloudWatch Logs
- Use CloudWatch Metrics to monitor build statistics
- Use EventBridge to detect failed builds and trigger notifications
- Use CloudWatch Alarms to notify if you need “thresholds” for failures
- Build Projects can be defined within CodePipeline or CodeBuild
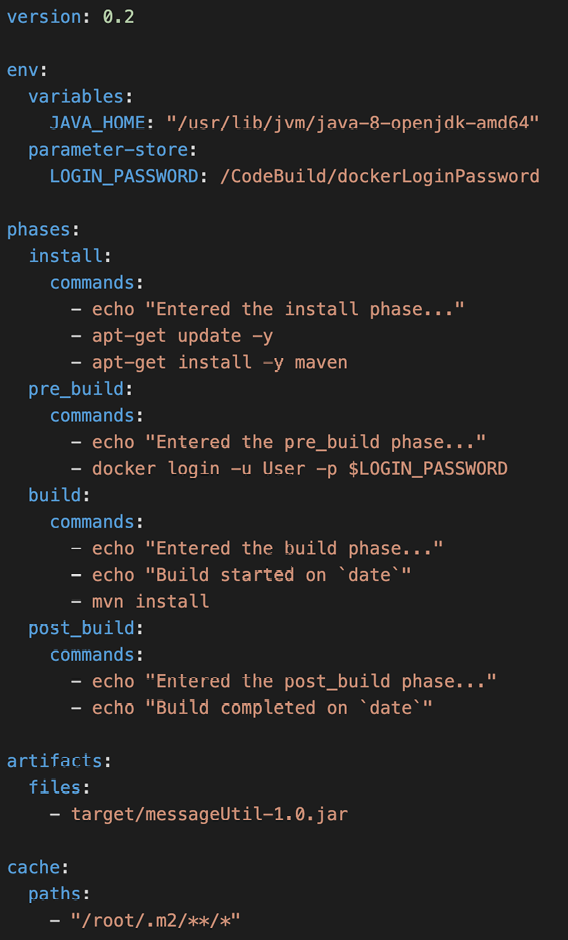
buildspec.yml
- buildspec.yml file must be at the root of your code
- env – define environment variables
- variables – plaintext variables
- parameter-store – variables stored in SSM Parameter Store
- secrets-manager – variables stored in AWS Secrets Manager
- phases – specify commands to run:
- install – install dependencies you may need for your build
- pre_build – final commands to execute before build
- Build – actual build commands
- post_build – finishing touches (e.g., zip output)
- artifacts – what to upload to S3 (encrypted with KMS)
- cache – files to cache (usually dependencies) to S3 for future build speedup
CodeDeploy��
- Deployment service that automates application deployment
- Deploy new applications versions to EC2 Instances, On-premises servers, Lambda functions, ECS Services
- Automated Rollback capability in case of failed deployments, or trigger CloudWatch Alarm
- Gradual deployment control
- A file named appspec.yml defines how the deployment happens
- Can deploy to EC2 Instances & on-premises servers
- Perform in-place deployments or blue/green deployments
- Must run the CodeDeploy Agent on the target instances
- Define deployment speed
- AllAtOnce: most downtime
- HalfAtATime: reduced capacity by 50%
- OneAtATime: slowest, lowest availability impact
- Custom: define your %
- Blue-Green Deployment: Create new Autoscaling Group and point with Load Balancer to it
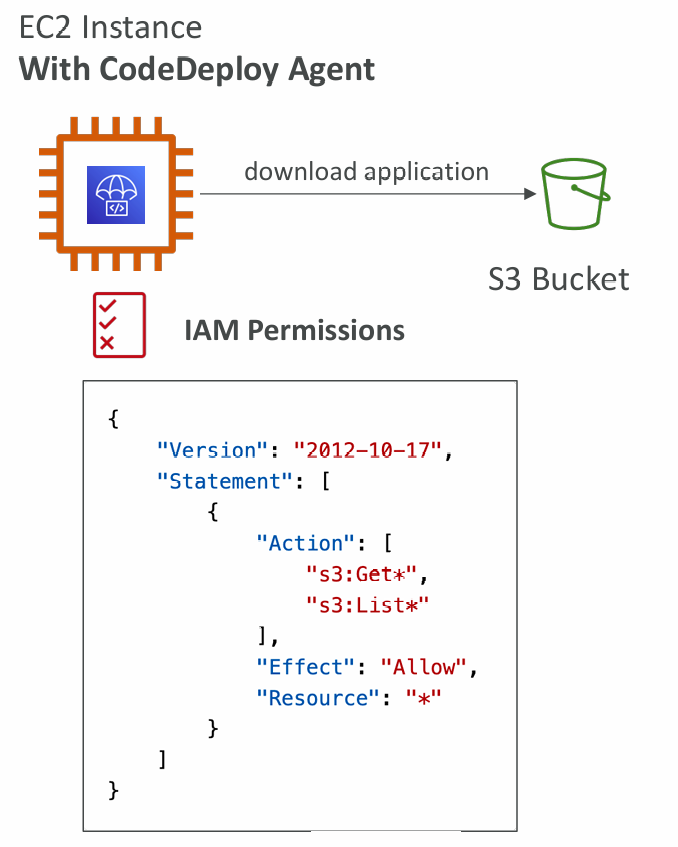
CodeDeploy Agent
- The CodeDeploy Agent must be running on the EC2 instances as a prerequisites
- It can be installed and updated automatically if you’re using Systems Manager
- The EC2 Instances must have sufficient permissions to access Amazon S3 to get deployment bundles
- CodeDeploy can help you automate traffic shift for Lambda aliases
- Feature is integrated within the SAM framework
- Linear: grow traffic every N minutes until 100%
- LambdaLinear10PercentEvery3Minutes
- LambdaLinear10PercentEvery10Minutes
- Canary: try X percent then 100%
- LambdaCanary10Percent5Minutes
- LambdaCanary10Percent30Minutes
- AllAtOnce: immediate
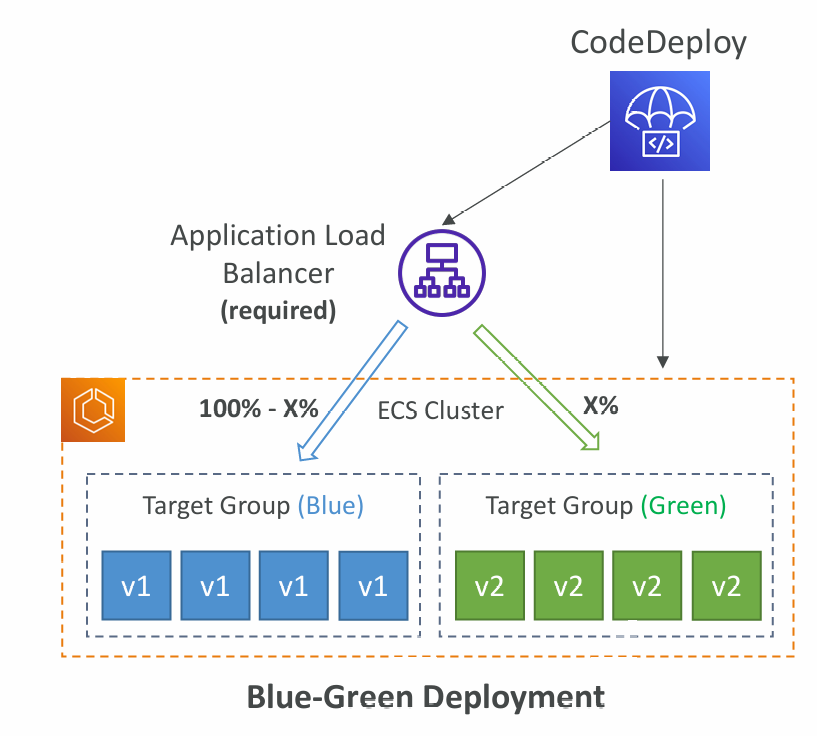
- CodeDeploy can help you automate the deployment of a new ECS Task Definition
- Only Blue/Green Deployments
- Linear: grow traffic every N minutes until 100%
- ECSLinear10PercentEvery3Minutes
- ECSLinear10PercentEvery10Minutes
- Canary: try X percent then 100%
- ECSCanary10Percent5Minutes
- ECSCanary10Percent30Minutes
- AllAtOnce: immediate
Deployment to EC2
- Define how to deploy the application using appspec.yml + Deployment Strategy
- Will do In-place update to your fleet of EC2 instances
- Can use hooks to verify the deployment after each deployment phase
Deploy to an ASG
- In-place Deployment
- Updates existing EC2 instances
- Newly created EC2 instances by an ASG will also get automated deployments
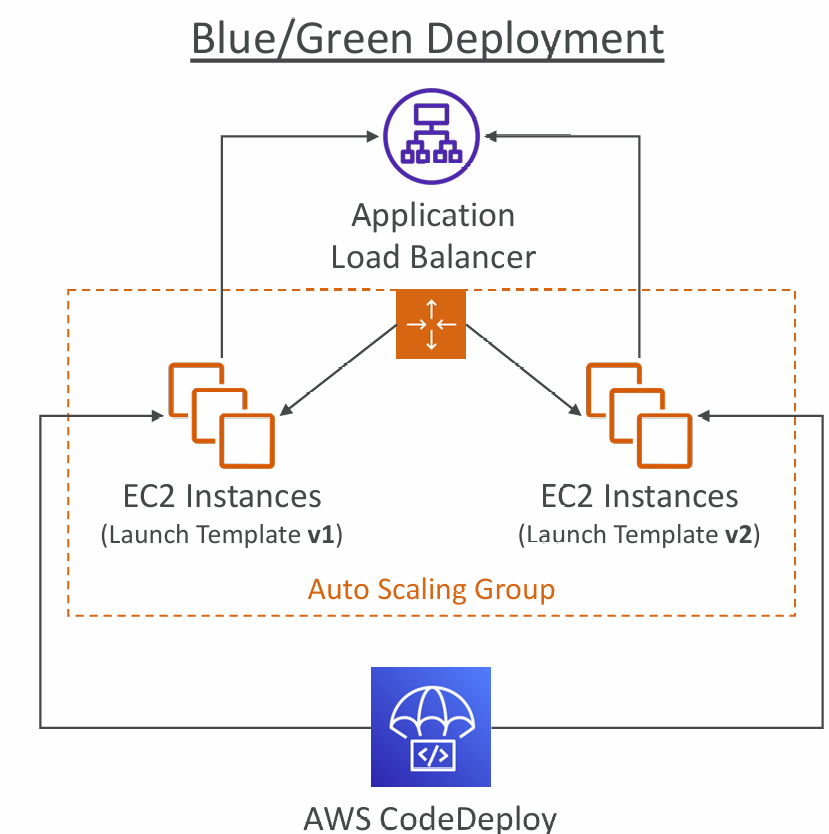
- Blue/Green Deployment
- A new Auto-Scaling Group is created (settings are copied)
- Choose how long to keep the old EC2 instances (old ASG)
- Must be using an ELB
Redeploy & Rollbacks
- Rollback = redeploy a previously deployed revision of your application
- Deployments can be rolled back:
- Automatically – rollback when a deployment fails or rollback when a CloudWatch Alarm thresholds are met
- Manually
- Disable Rollbacks — do not perform rollbacks for this deployment
- If a roll back happens, CodeDeploy redeploys the last known good revision as a new deployment (not a restored version)
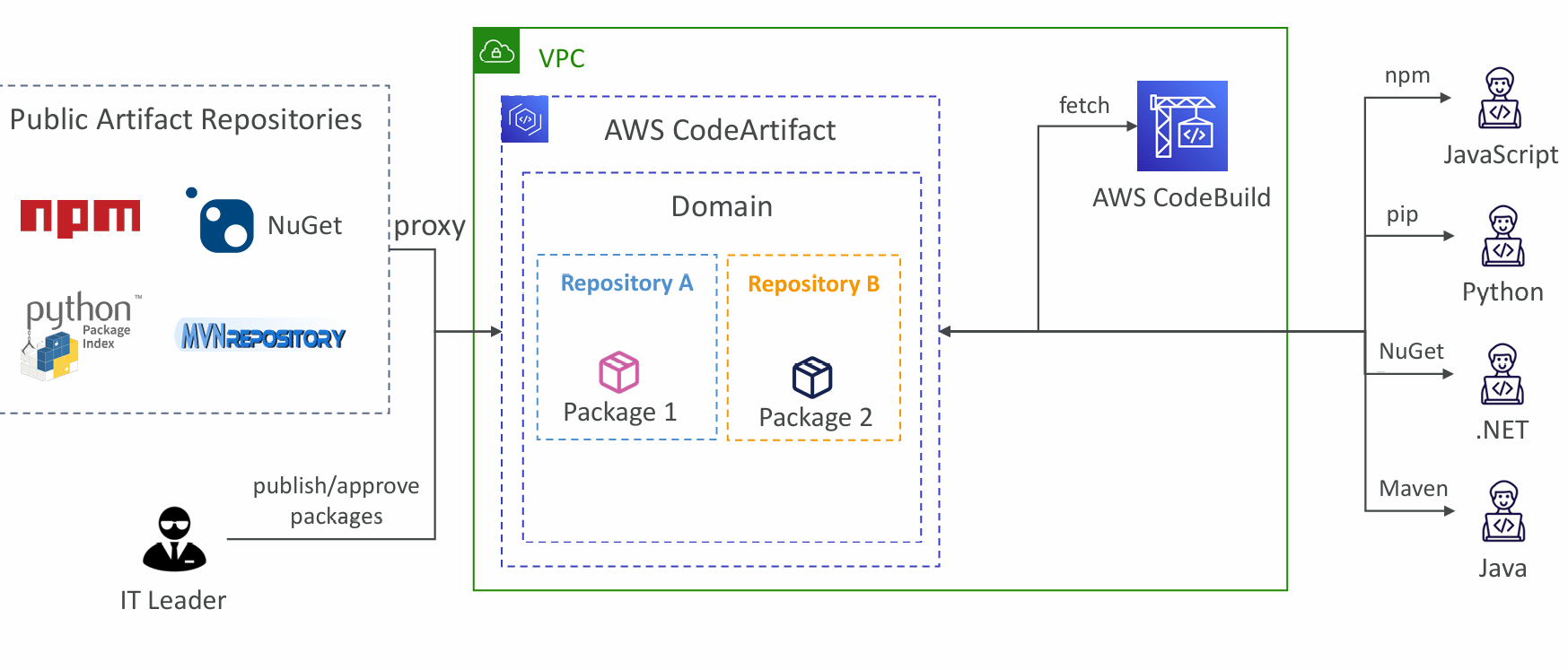
CodeArtifact
- Software packages depend on each other to be built (also called code dependencies), and new ones are created
- Storing and retrieving these dependencies is called artifact management
- Traditionally you need to setup your own artifact management system
- CodeArtifact is a secure, scalable, and cost-effective artifact management for software development
- Works with common dependency management tools such as Maven, Gradle, npm, yarn, twine, pip, and NuGet
- Developers and CodeBuild can then retrieve dependencies straight from CodeArtifact
EventBridge Integration
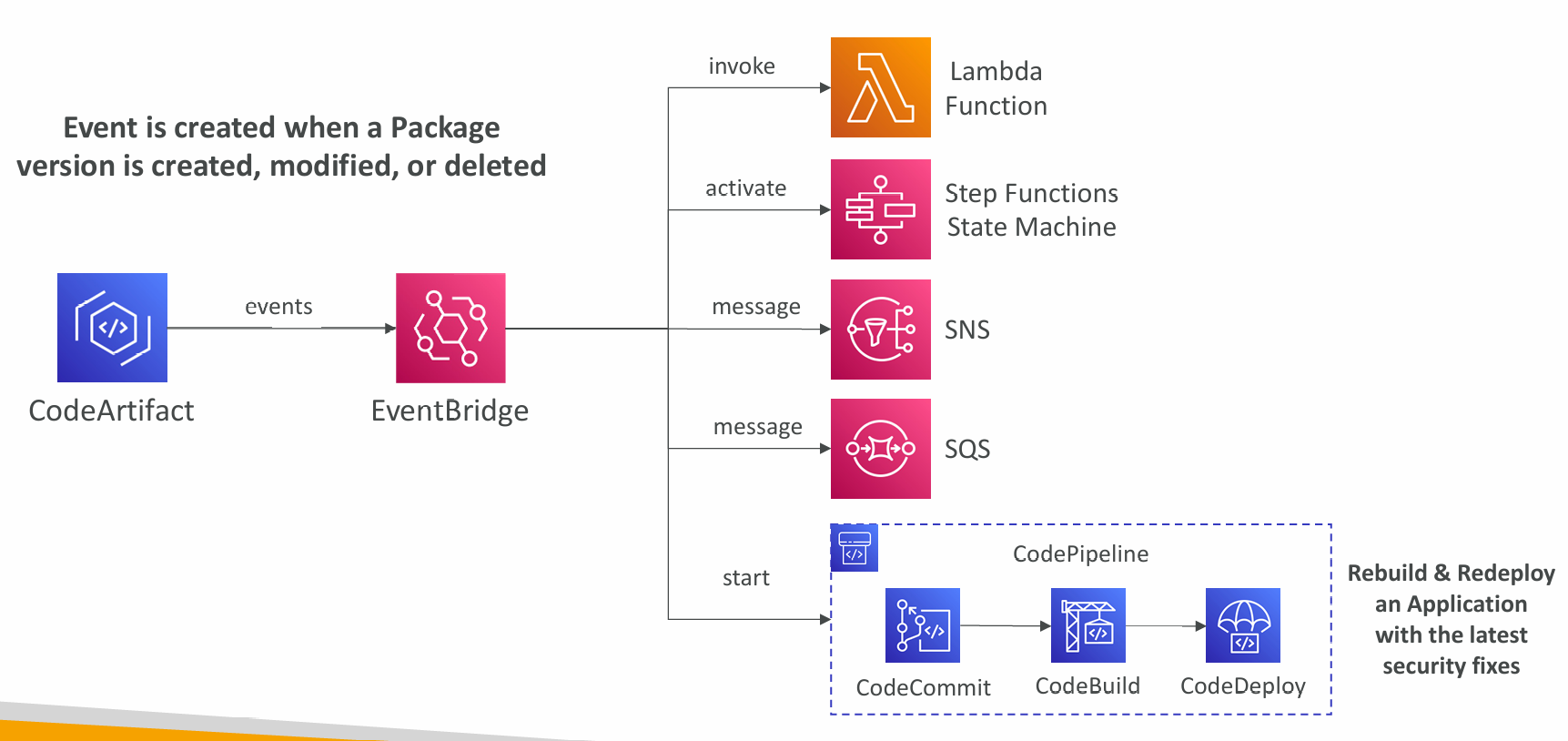
Resource Policy
- Can be used to authorize another account to access CodeArtifact
- A given principal can either read all the packages in a repository or none of them
CodeGuru
- An ML-powered service for automated code reviews and application performance recommendations
- Provides two functionalities
- CodeGuru Reviewer: automated code reviews for static code analysis (development)
- CodeGuru Profiler: visibility/recommendations about application performance during runtime (production)
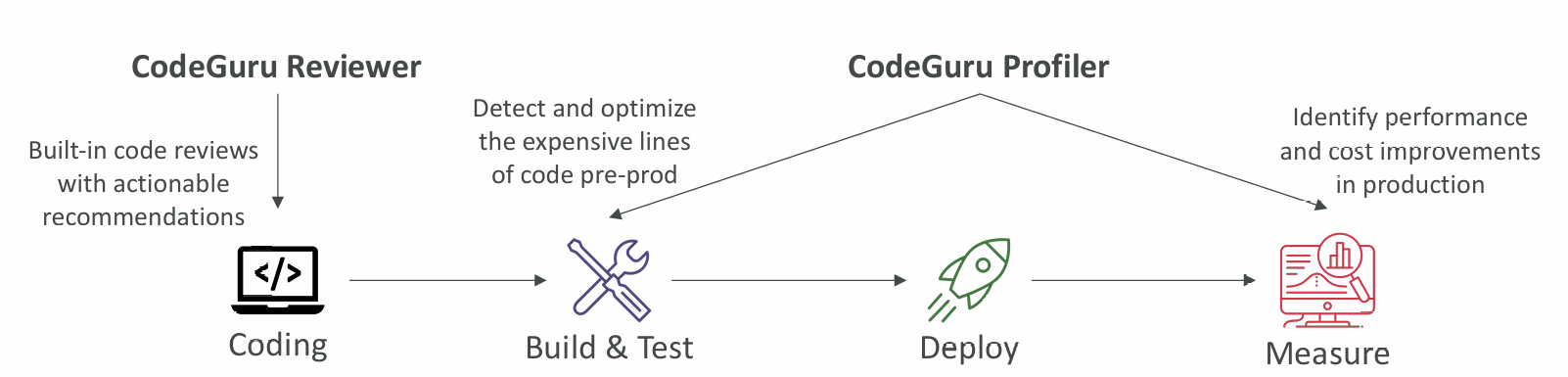
Reviewer
- Identify critical issues, security vulnerabilities, and hard-to-find bugs
- Example: common coding best practices, resource leaks, security detection, input validation
- Uses Machine Learning and automated reasoning
- Hard-learned lessons across millions of code reviews on 1000s of open-source and Amazon repositories
- Supports Java and Python
- Integrates with GitHub, Bitbucket, and AWS CodeCommit
Profiler
- Helps understand the runtime behavior of your application
- Example: identify if your application is consuming excessive CPU capacity on a logging routine
- Features:
- Identify and remove code inefficiencies
- Improve application performance (e.g., reduce CPU utilization)
- Decrease compute costs
- Provides heap summary (identify which objects using up memory)
- Anomaly Detection
- Support applications running on AWS or on premise
- Minimal overhead on application
Agent Configuration
- MaxStackDepth – the maximum depth of the stacks in the code that is represented in the profile
- Example: if CodeGuru Profiler finds a method A, which calls method B, which calls method C, which calls method D, then the depth is 4
- If the MaxStackDepth is set to 2, then the profiler evaluates A and B
- MemoryUsageLimitPercent – the memory percentage used by the profiler
- MinimumTimeForReportingInMilliseconds – the minimum time between sending reports (milliseconds)
- ReportingIntervalInMilliseconds – the reporting interval used to report profiles (milliseconds)
- SamplingIntervalInMilliseconds – the sampling interval that is used to profile samples (milliseconds)
- Reduce to have a higher sampling rate









