AWS CLI, SDK, IAM Roles & Policies
EC2 Instance Metadata (IMDS)
- AWS EC2 Instance Metadata (IMDS) is powerful but one of the least known features to developers
- It allows AWS EC2 instances to ”learn about themselves” without using an IAM Role for that purpose
- The URL is http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data
- You can retrieve the IAM Role name from the metadata, but you CANNOT retrieve the IAM Policy
- Metadata = Info about the EC2 instance
- Userdata = launch script of the EC2 instance
IMDSv2 vs. IMDSv1
- IMDSv1 is accessing http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data directly
- IMDSv2 is more secure and is done in two steps
- Get Session Token (limited validity) – using headers & PUT
- Use Session Token in IMDSv2 calls – using headers
MFA with CLI
- To use MFA with the CLI, you must create a temporary session
- To do so, you must run the STS GetSessionToken API call
- aws sts get-session-token --serial-number arn-of-the-mfa-device --token-code code-from-token --duration-seconds 3600
AWS SDK
- Used to perform actions on AWS directly from your applications code
- Official SDKs are .NET, Java, PHP, Go, Python, etc.
SDK Overview
- We have to use the AWS SDK when coding against AWS Services such as DynamoDB
- The AWS CLI uses the Python SDK (boto3)
- The exam expects you to know when you should use an SDK
- Good to know: if you don’t specify or configure a default region, then us-east-1 will be chosen by default
AWS Limits (Quotas)
- API Rate Limits
- DescribeInstances API for EC2 has a limit of 100 calls per seconds
- GetObject on S3 has a limit of 5500 GET per second per prefix
- For Intermittent Errors: implement Exponential Backoff
- For Consistent Errors: request an API throttling limit increase
- Service Quotas (Service Limits)
- Running On-Demand Standard Instances: 1152 vCPU
- You can request a ser vice limit increase by opening a ticket
- You can request a ser vice quota increase by using the Service Quotas API
- Retry mechanism already included in AWS SDK API calls
- Must implement yourself if using the AWS API as-is or in specific cases
- Must only implement the retries on 5xx server errors and throttling
- Do not implement on the 4xx client errors
AWS CLI Credentials Provider Chain
The CLI will look for credentials in this order:
- Command line options: --region,--output, and--profile
- Environment variables: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY, and AWS_SESSION_TOKEN
- CLI credentials file: aws configure ~/.aws/credentials on Linux / Mac & C:\Users\user.aws\credentials on Windows
- CLI configuration file:– aws configure ~/.aws/config on Linux / macOS & C:\Users\USERNAME.aws\config on Windows
- Container credentials: for ECS tasks
- Instance profile credentials: for EC2 Instance Profiles
Default Credentials Provider Chain
The Java SDK (example) will look for credentials in this order:
- Java system properties: aws.accessKeyId and aws.secretKey
- Environment variables: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID andAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
- The default credential profiles file – ex at: ~/.aws/credentials, shared by many SDK
- Amazon ECS container credentials – for ECS containers
- Instance profile credentials: used on EC2 instances
AWS Credentials Scenario
- An application deployed on an EC2 instance is using environment variables with credentials from an IAM user to call the Amazon S3 API
- The IAM user has S3FullAccess permissions
- The application only uses one S3 bucket, so according to best practices
- An IAM Role & EC2 Instance Profile was created for the EC2 instance
- The Role was assigned the minimum permissions to access that one S3 bucket
The IAM Instance Profile was assigned to the EC2 instance, but it still had access to all S3 buckets. Why?
Answer: The credentials chain is still giving priorities to the environment variables
AWS Credentials Best Practices
- Best practice is for credentials to be inherited from the credentials chain
- If using working within AWS, use IAM Roles
- EC2 Instances Roles for EC2 Instances
- ECS Roles for ECS tasks
- Lambda Roles for Lambda functions
- If working outside of AWS, use environment variables / named profiles
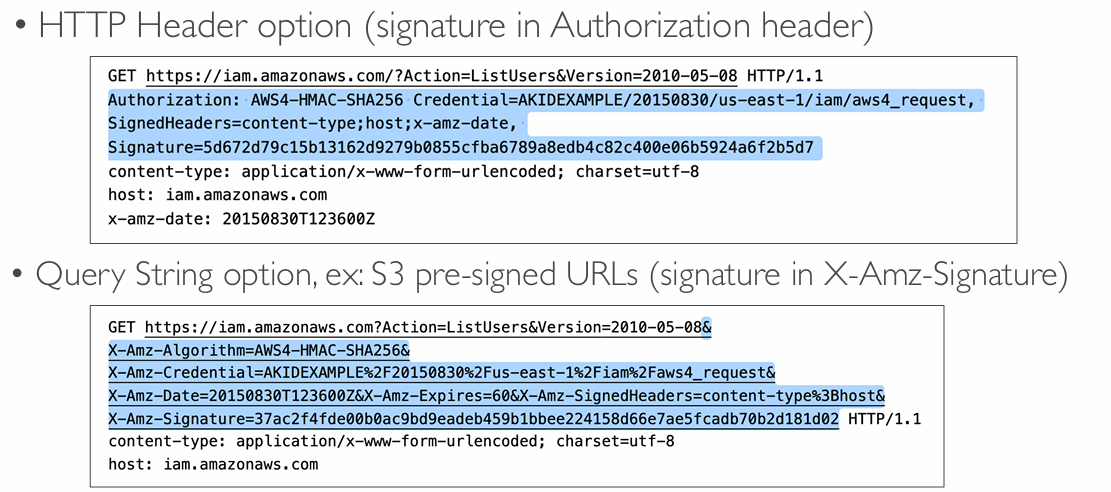
Signing AWS API requests
- When you call the AWS HTTP API, you sign the request so that AWS can identify you, using your AWS credentials (access key & secret key)
- Note: some requests to Amazon S3 don’t need to be signed
- If you use the SDK or CLI, the HTTP requests are signed for you
- You should sign an AWS HTTP request using Signature v4 (SigV4)
SigV4 Request examples