Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Users and Groups
- Root account: created by default, shouldn't be used or shared
- Users: People in organization which can be grouped (must not be in group)
- Groups: Groups only contain users, not other groups
Permissions
- Users and Groups can be assigned JSON documents called policies
- These policies define the permissions of the users
- In AWS we apply the least privilege principle: Don't give more permissions than necessary
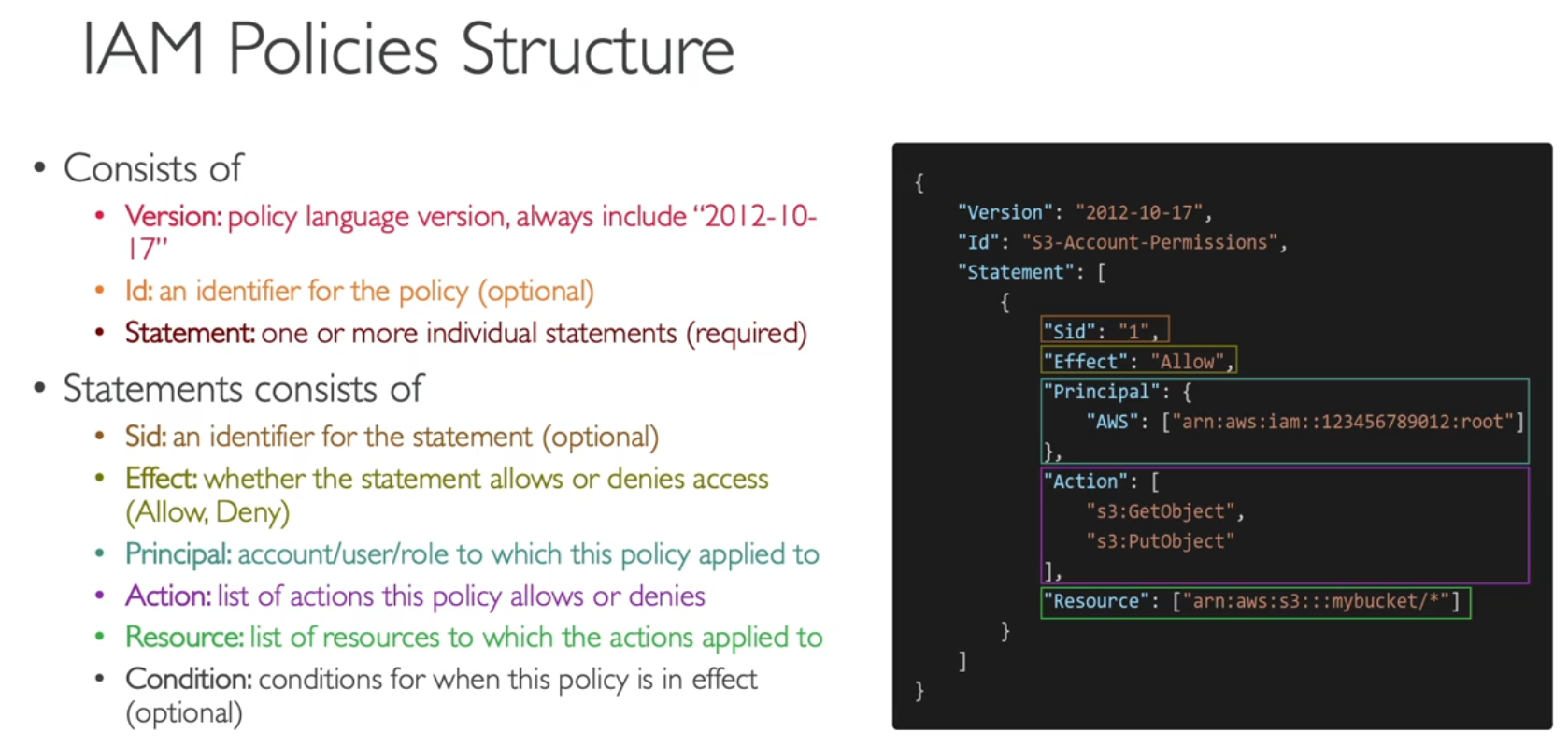
IAM Policies
- JSON document that outlines permissions for users or groups
- Policies can be applied at group or user level
- Policies give the users a given list of permissions
Policy Structure
Example Policy: AdministratorAccess
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "*",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Password Policy
- In AWS, you can setup a password policy to
- set minimum password length
- require specific character types
- allow all IAM users to change their own passwords
- require users to change their password after some time
- prevent password re-use
Multi Factor Authentication
- You want to protect your Root Accounts and IAM users
- MFA = password you know + security device you own
- Options:
- Virtual MFA Device (e.g. Goole Authenticator)
- Universal 2nd Factor (U2F) Security Key (e.g. YubiKey)
- Hardware Key Fob MFA Device
- Hardware Key Fob MFA Device for AWS GovCloud (US)
How can users access AWS
- To access AWS, you have three options
- AWS Management Console (protected by password + MFA)
- AWS Command Line Interface (CLI): protected by access keys
- AWS Software Developer Kit (SDK) - for code: protected by access keys
- Access Keys are generated through the AWS Console
- Users manage their own access keys
IAM Roles
- Like groups but for services
- Needed because some AWS service will need to perform actions on your behalf
- Common roles:
- EC2 Instance Roles
- Lambda Function Roles
- Roles for CloudFormation
IAM Security Tools
- IAM Credentials Report (account-level)
- a report that lists all your account's users and the status of their various credentials
- IAM Access Advisor (user-level)
- Access advisor shows the service permissions granted to a user and when those services were last accessed
- You can use this information to revise your policies
Shared Responsibility Model for IAM
Who is responsible for what?
- AWS
- Infrastructure (global network security)
- Configuration and vulnerability analysis
- Compliance validation
- You
- Users, Groups, Roles, Policies management and monitoring
- Enable MFA on all accounts
- Rotate all your keys often
- Use IAM tools to apply appropriate permissions
- Analyze access patterns & review permissions
Summary
- Users: mapped to a physical user, has a password for AWS Console
- Groups: contains users only
- Policies: JSON document that outlines permissions for users or groups
- Roles: for EC2 instances or AWS services
- Security: MFA + Password Policy
- AWS CLI: manage your AWS services using the command-line
- AWS SDK: manage your AWS services using a programming language
- Access Keys: access AWS using the CLI or SDK
- Audit: IAM Credential Reports & IAM Access Advisor